ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(11):4289-4300. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70002 This issue Cite
Research Paper
High Glucose Accelerates Tumor Progression by Regulating MEDAG-Mediated Autophagy Levels in Breast Cancer
1. Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, P. R. China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, P. R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
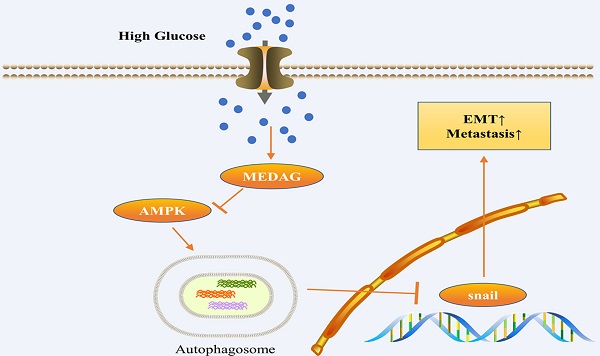
Recent studies have shown that diabetes is a major risk factor for breast cancer (BC), but the mechanism is incompletely understood. Mesenteric estrogen-dependent adipogenesis (MEDAG) plays a significant role in both glucose uptake and BC development. However, the relationship between MEDAG and BC under high glucose (HG) conditions remains unclear. In our study, MEDAG expression was higher in BC tissue from diabetic patients than in BC tissue from nondiabetic patients. HG promoted BC progression in vitro and in vivo by upregulating MEDAG expression. Furthermore, MEDAG deficiency increased the autophagosome number and autophagic flux. Moreover, inhibition of autophagy partially reversed MEDAG knockdown (MEDAGKD)-induced suppression of tumorigenic biological behaviors and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression. Finally, MEDAG significantly suppressed AMPK phosphorylation. Additionally, the AMPK inhibitor Compound C markedly reduced autophagosome accumulation and antitumor effects in MEDAGKD cells. Treatment with the AMPK activator AICAR exhibited similar effects in MEDAG-overexpressing (MEDAGOE) cells. In conclusion, the MEDAG-AMPK-autophagy axis is vital to BC progression in diabetic patients. Our findings provide a novel treatment target for BC in patients with diabetes.
Keywords: breast cancer, diabetes, MEDAG, EMT, AMPK signaling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact