10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(11):4513-4531. doi:10.7150/ijbs.75298 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Maternal EHMT2 is essential for homologous chromosome segregation by regulating Cyclin B3 transcription in oocyte meiosis
1. Fertility Preservation Lab, Guangdong-Hong Kong Metabolism & Reproduction Joint Laboratory, Reproductive Medicine Center, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, 510317, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
3. Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, Beijing 100084, China.
4. Center for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
5. Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Shanghai East Hospital, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Signaling and Disease Research, Frontier Science Center for Stem Cell Research, School of Life Sciences and Technology, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200120, China.
6. The Affiliated Tai'an City Central Hospital of Qingdao University, Taian, Shandong, 271000, China.
7. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
8. Center for Clinical Medicine Research, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 6460000, China.
9. State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Institute of Zoology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
10. Department of Veterinary Pathobiology, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO 65211, USA.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
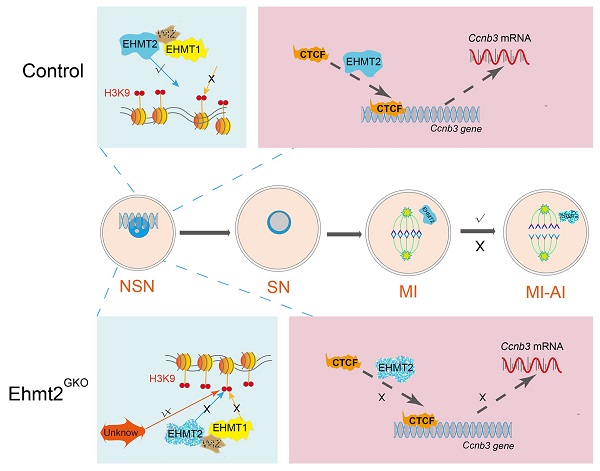
During oocyte growth, various epigenetic modifications are gradually established, accompanied by accumulation of large amounts of mRNAs and proteins. However, little is known about the relationship between epigenetic modifications and meiotic progression. Here, by using Gdf9-Cre to achieve oocyte-specific ablation of Ehmt2 (Euchromatic-Histone-Lysine-Methyltransferase 2) from the primordial follicle stage, we found that female mutant mice were infertile. Oocyte-specific knockout of Ehmt2 caused failure of homologous chromosome separation independent of persistently activated SAC during the first meiosis. Further studies revealed that lacking maternal Ehmt2 affected the transcriptional level of Ccnb3, while microinjection of exogenous Ccnb3 mRNA could partly rescue the failure of homologous chromosome segregation. Of particular importance was that EHMT2 regulated ccnb3 transcriptions by regulating CTCF binding near ccnb3 gene body in genome in oocytes. In addition, the mRNA level of Ccnb3 significantly decreased in the follicles microinjected with Ctcf siRNA. Therefore, our findings highlight the novel function of maternal EHMT2 on the metaphase I-to-anaphase I transition in mouse oocytes: regulating the transcription of Ccnb3.
Keywords: EHMT2/G9a, Cyclin B3, transcriptional regulation, oocyte, meiosis, homologous chromosome segregation, CTCF

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact