10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(11):4545-4559. doi:10.7150/ijbs.71287 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lithocholic acid inhibits dendritic cell activation by reducing intracellular glutathione via TGR5 signaling
The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Chongqing Eye Institute, and Chongqing Branch of National Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases, Chongqing, P. R. China.
Abstract
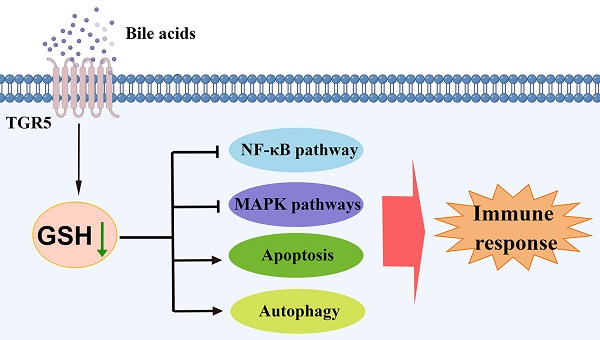
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the major antigen-presenting cells and play an important role in autoimmune uveitis. Emerging evidence suggests that bile acids (BAs) regulate DCs maturation. However, the underlying mechanisms by which BAs regulate the function of DCs still need to be clarified. Here, we demonstrate that lithocholic acid (LCA) inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the expression of surface molecules in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs). LCA attenuates the severity of EAU by modulating the maturation of splenic CD11C+MHCIIhigh DCs. Notably, Takeda G-protein coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) deficiency partially reverses the inhibitory effect of LCA on DCs in vitro and in vivo. TGR5 activation also downregulates the NF-κB and MAPK pathways by inhibiting glutathione production and inducing oxidative stress in DCs, which leads to apoptosis and autophagy in DCs. In addition, LCA or INT-777 treatment increases the TGR5 expression in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MD-DCs) of patients with active BD, whereas both LCA and TGR5 agonists inhibit the activation of MD-DCs. These results suggest that LCA and TGR5 agonists might be potential therapeutic drugs for the treatment of autoimmune uveitis.
Keywords: Dendritic cells, Bile acids, TGR5, Uveitis, Autoimmune disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact