10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(13):5001-5018. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70149 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ALKBH5/MAP3K8 axis regulates PD-L1+ macrophage infiltration and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression
1. Hepatobiliary Surgery Department, Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400010, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400010, China.
3. Department of Gastroenterology, Chongqing University Central Hospital (Chongqing Emergency Medical Center), Chongqing 400010, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
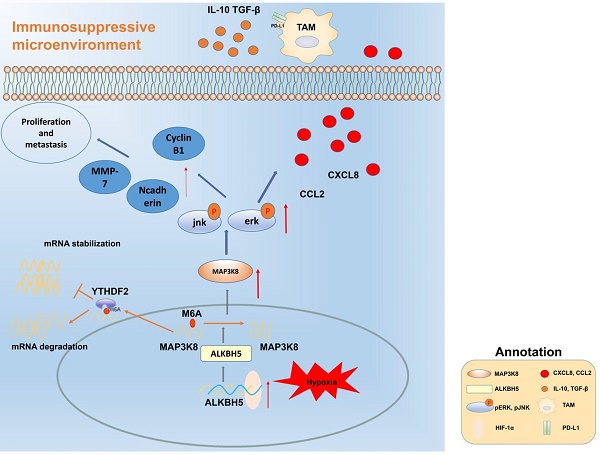
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common malignant tumors.M6A is a novel epigenetic modification that have been emerged as vital regulators for the progression of HCC. However, the regulatory role, clinical significance and the details of the modification, such as the impact on the local tumor environment, remain largely unclear. Our study showed that ALKBH5 was highly expressed in HCC and high ALKBH5 expression predicted a worse prognosis of HCC patients. Prediction of ALKBH5 function by tissue samples and single cell sequencing Gene Set Variation Analysis. Primary CD3 + T lymphocytes and bone marrow-derived macrophages were used to evaluate the effect of ALKBH5 on immune microenvironment. The results indicated that ALKBH5 promote HCC cell proliferation, metastasis and PD-L1+macrophage recruitment. Mechanistically the results showed that ALKBH5 regulates MAP3K8 expression in a m6A dependent manner which mediates the proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells. ALKBH5 also promotes the activation of JNK and ERK pathways through upregulating MAP3K8, thus regulating the expression of IL-8 and promoting macrophage recruitment. Taken together, these data show that ALKBH5 promotes HCC growth, metastasis and macrophage recruitment through ALKBH5/MAP3K8 axis and it may serve as a potential diagnostic marker and target for treatment of HCC patients.
Keywords: M6A, Hypoxia, Tumor-associated macrophages, Immune microenvironment, PD-L1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact