10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(13):5123-5135. doi:10.7150/ijbs.66673 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Decrease of circARID1A retards glioblastoma invasion by modulating miR-370-3p/ TGFBR2 pathway
1. The National Key Clinical Specialty, The Engineering Technology Research Center of Education Ministry of China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory on Brain Function Repair and Regeneration, Department of Neurosurgery, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, China.
2. Department of Neurosurgery, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, South China University of Technology, Foshan 528200, China.
3. Department of Neurosurgery, Huizhou Municipal Central Hospital, Huizhou Shi, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
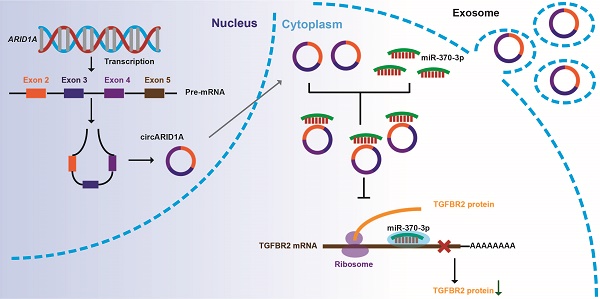
Increasing evidence suggests that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in regulating tumor biological activity. Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most lethal diseases characterized by highly aggressive proliferative and invasive behaviors. We aimed to explore how circRNAs influenced GBM biological activity. By circRNA array analysis we found that circARID1A was significantly up-regulated in GBM. Next, we found that circARID1A was up-regulated in GBM tissues and cell lines. Interfering with circARID1A inhibited the migration and invasion of a human GBM cell line U87. By performing dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA pull-down and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), we determined that circARID1A directly bound to miR-370-3p. Moreover, we confirmed that transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2) was the target gene of miR-370-3p by performing RNA pull-down, dual-luciferase reporter assays and western blotting. Further experiments verified that circARID1A promoted GBM cell migration and invasion by modulating miR-370-3p/ TGFBR2 pathway. In addition, we demonstrated that silencing circARID1A restrain the growth of GBM in vivo. Finally, we showed that circARID1A was abundant in GBM cell derived exosomes. In conclusion, circARID1A participated in regulating migration and invasion of GBM via modulation of miR-370-3p/ TGFBR2 and thus may be a potential serum biomarker of GBM.
Keywords: circARID1A, miR-370-3p, TGFBR2, glioblastoma, exosomes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact