ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(13):5168-5184. doi:10.7150/ijbs.74430 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tubule-mitophagic secretion of SerpinG1 reprograms macrophages to instruct anti-septic acute kidney injury efficacy of high-dose ascorbate mediated by NRF2 transactivation
1. Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Center, Department of Intensive Care Unit, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
2. Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
3. Department of Pathology, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
4. Clinical Research Institute, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
5. Center for Rehabilitation Medicine, Department of Intensive Rehabilitation Care Unit, Zhejiang P rovincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
6. Center for Rehabilitation Medicine, Rehabilitation & Sports Medicine Research Institute of Zhejiang Province, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang, P.R.China.
Abstract
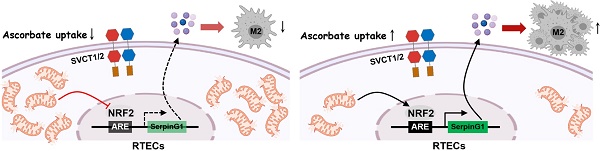
High-dose ascorbate confers tubular mitophagy responsible for septic acute kidney injury (AKI) amelioration, yet its biological roles in immune regulation remain poorly understood.
Methods: The role of tubular mitophagy in macrophage polarization upon high-dose ascorbate treatment was assessed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis (FACS) in vitro and by immunofluorescence in AKI models of LPS-induced endotoxemia (LIE) from Pax8-cre; Atg7flox/flox mice. The underlying mechanisms were revealed by RNA-sequencing, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), luciferase reporter, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and adeno-associated viral vector serotype 9 (AAV9) delivery assays.
Results: High-dose ascorbate enables conversion of macrophages from a pro-inflammatory M1 subtype to an anti-inflammatory M2 subtype in murine AKI models of LIE, leading to decreased renal IL-1β and IL-18 production, reduced mortality and alleviated tubulotoxicity. Blockade of tubular mitophagy abrogates anti-inflammatory macrophages polarization under the high-dose ascorbate-exposed coculture systems. Similar abrogations are verified in LIE mice with tubular epithelium-specific ablation of Atg7, where the high-dose ascorbate-inducible renal protection and survival improvement are substantially weaker than their control littermates. Mechanistically, high-dose ascorbate stimulates tubular secretion of serpin family G member 1 (SerpinG1) through maintenance of mitophagy, for which nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 (NRF2) transactivation is required. SerpinG1 perpetuates anti-inflammatory macrophages to prevent septic AKI, while kidney-specific disruption of SerpinG1 by adeno-associated viral vector serotype 9 (AAV9)-short hairpin RNA (shRNA) delivery thwarts the anti-inflammatory macrophages polarization and anti-septic AKI efficacy of high-dose ascorbate.
Conclusion: Our study identifies SerpinG1 as an intermediate of tubular mitophagy-orchestrated myeloid function during septic AKI and reveals a novel rationale for ascorbate-based therapy.
Keywords: septic acute kidney injury, tubular mitophagy, macrophage, high-dose ascorbate, serpin family G member 1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact