10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(14):5475-5488. doi:10.7150/ijbs.73790 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting Ferroptosis by Ubiquitin System Enzymes: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer
1. Department of Dermatology, Hunan Engineering Research Center of Skin Health and Disease, Hunan Key Laboratory of Skin Cancer and Psoriasis, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
2. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
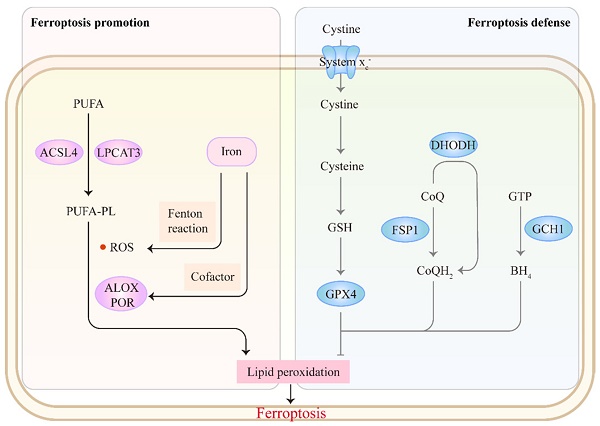
Ferroptosis is a novel type of regulated cell death driven by the excessive accumulation of iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. Therapy-resistant tumor cells, particularly those in the mesenchymal-like state and prone to metastasis, are highly susceptible to ferroptosis, suggesting that induction of ferroptosis in tumor cells is a promising strategy for cancer therapy. Although ferroptosis is regulated at various levels, ubiquitination is key to post-translational regulation of ferroptotic cell death. E3 ubiquitin ligases (E3s) and deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are the most remarkable ubiquitin system enzymes, whose dysregulation accounts for the progression of multiple cancers. E3s are involved in the attachment of ubiquitin to substrates for their degradation, and this process is reversed by DUBs. Accumulating evidence has highlighted the important role of ubiquitin system enzymes in regulating the sensitivity of ferroptosis. Herein, we will portray the regulatory networks of ferroptosis mediated by E3s or DUBs and discuss opportunities and challenges for incorporating this regulation into cancer therapy.
Keywords: Ferroptosis, E3 ubiquitin ligase, Deubiquitinating enzyme, Cancer therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact