10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(1):156-166. doi:10.7150/ijbs.76148 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A stapled chromogranin A-derived peptide homes in on tumors that express αvβ6 or αvβ8 integrins
1. Division of Experimental Oncology, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy.
2. Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy.
3. Experimental Imaging Center, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy.
4. Istituto di Scienze e Tecnologie Chimiche, C.N.R., Milan, Italy.
5. Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy.
6. Division of Immunology Transplantation and Infectious Diseases, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy.
7. Lung Biology Center, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA.
8. Institute of Molecular Bioimaging and Physiology of C.N.R., Segrate, Italy.
9. Faculty of Medicine and Surgery, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy.
Abstract
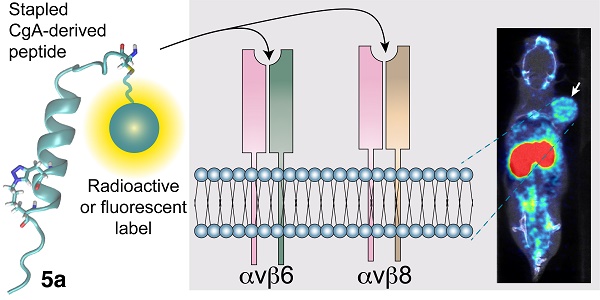
Rationale: The αvβ6- and αvβ8-integrins, two cell-adhesion receptors upregulated in many tumors and involved in the activation of the latency associated peptide (LAP)/TGFβ complex, represent potential targets for tumor imaging and therapy. We investigated the tumor-homing properties of a chromogranin A-derived peptide containing an RGDL motif followed by a chemically stapled alpha-helix (called “5a”), which selectively recognizes the LAP/TGFβ complex-binding site of αvβ6 and αvβ8.
Methods: Peptide 5a was labeled with IRDye 800CW (a near-infrared fluorescent dye) or with 18F-NOTA (a label for positron emission tomography (PET)); the integrin-binding properties of free peptide and conjugates were then investigated using purified αvβ6/αvβ8 integrins and various αvβ6/αvβ8 single - or double-positive cancer cells; tumor-homing, biodistribution and imaging properties of the conjugates were investigated in subcutaneous and orthotopic αvβ6-positive carcinomas of the pancreas, and in mice bearing subcutaneous αvβ8-positive prostate tumors.
Results: In vitro studies showed that 5a can bind both integrins with high affinity and inhibits cell-mediated TGFβ activation. The 5a-IRDye and 5a-NOTA conjugates could bind purified αvβ6/αvβ8 integrins with no loss of affinity compared to free peptide, and selectively recognized various αvβ6/αvβ8 single- or double-positive cancer cells, including cells from pancreatic carcinoma, melanoma, oral mucosa, bladder and prostate cancer. In vivo static and dynamic optical near-infrared and PET/CT imaging and biodistribution studies, performed in mice with subcutaneous and orthotopic αvβ6-positive carcinomas of the pancreas, showed high target-specific uptake of fluorescence- and radio-labeled peptide by tumors and low non-specific uptake in other organs and tissues, except for excretory organs. Significant target-specific uptake of fluorescence-labeled peptide was also observed in mice bearing αvβ8-positive prostate tumors.
Conclusions: The results indicate that 5a can home to αvβ6- and/or αvβ8-positive tumors, suggesting that this peptide can be exploited as a ligand for delivering imaging or anticancer agents to αvβ6/αvβ8 single- or double-positive tumors, or as a tumor-homing inhibitor of these TGFβ activators.
Keywords: RGD motif, αvβ6 and αvβ8 integrins, TGFβ, chromogranin A, cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact