Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(2):521-536. doi:10.7150/ijbs.80200 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Neuropeptide Y protects kidney from acute kidney injury by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R-NF-κB-Mincle-dependent mechanism
1. Research Center of Intergated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, 646000, China.
2. Institute of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, 646000, China.
3. Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
4. Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for Immunological and Genetic Kidney Disease, Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, 510080, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
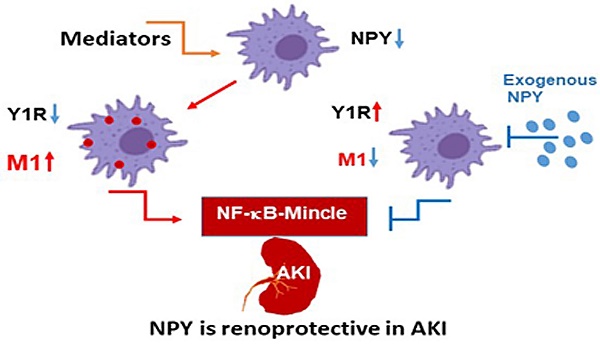
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is produced by the nerve system and may contribute to the progression of CKD. The present study found the new protective role for NPY in AKI in both patients and animal models. Interestingly, NPY was constitutively expressed in blood and resident kidney macrophages by co-expressing NPY and CD68+ markers, which was lost in patients and mice with AKI-induced by cisplatin. Unexpectedly, NPY was renoprotective in AKI as mice lacking NPY developed worse renal necroinflammation and renal dysfunction in cisplatin and ischemic-induced AKI. Importantly, NPY was also a therapeutic agent for AKI because treatment with exogenous NPY dose-dependently inhibited cisplatin-induced AKI. Mechanistically, NPY protected kidney from AKI by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R-NF-κB-Mincle-dependent mechanism as deleting or silencing NPY decreased Y1R but increased NF-κB-Mincle-mediated M1macrophage activation and renal necroinflammation, which were reversed by addition of NPY or by silencing Mincle but promoted by blocking Y1R with BIBP 3226. Thus, NPY is renoprotective and may be a novel therapeutic agent for AKI. NPY may act via Y1R to protect kidney from AKI by blocking NF-κB-Mincle-mediated M1 macrophage activation and renal necroinflammation.
Keywords: Neuropeptide Y, Y1R, AKI, Inflammation, Macrophage, Mincle

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact