10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(3):721-743. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79063 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Extracellular vesicles, the emerging mirrors of brain physiopathology
1. Ace Alzheimer Center Barcelona - International University of Catalunya (UIC), Barcelona, Spain
2. Biomedical Research Networking Centre in Neurodegenerative Diseases (CIBERNED), Madrid, Spain.
3. Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (IN2UB), Barcelona, Spain.
4. Department of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Technology and Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences, University of Barcelona, Spain.
5. Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutic Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences, University of Barcelona, Spain.
6. Biosensing and Bioanalysis Group, Institut de Biotecnologia i de Biomedicina (IBB-UAB), Mòdul B Parc de Recerca UAB, Campus Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193 Bellaterra, Spain.
7. Grup de Sensors i Biosensors, Departament de Química, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193 Bellaterra, Spain.
8. Unit of Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Peptides, IQAC-CSIC, 08034 Barcelona, Spain.
9. Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal.
10. REQUIMTE/UCIBIO, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal.
Abstract
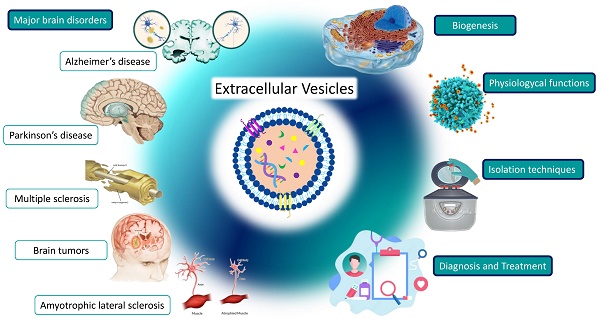
Extracellular vesicles are secreted by a wide variety of cells, and their primary functions include intercellular communication, immune responses, human reproduction, and synaptic plasticity. Their molecular cargo reflects the physiological processes that their cells of origin are undergoing. Thus, many studies have suggested that extracellular vesicles could be a promising biomarker tool for many diseases, mainly due to their biological relevance and easy accessibility to a broad range of body fluids. Moreover, since their biological composition leads them to cross the blood-brain barrier bidirectionally, growing evidence points to extracellular vesicles as emerging mirrors of brain diseases processes. In this regard, this review explores the biogenesis and biological functions of extracellular vesicles, their role in different physiological and pathological processes, their potential in clinical practice, and the recent outstanding studies about the role of exosomes in major human brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or brain tumors.
Keywords: Exosomes, extracellular vesicles, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, glioblastoma, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, neurodegenerative diseases

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact