10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(3):811-828. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79928 This issue Cite
Review
Novel insight into metabolic reprogrammming in cancer radioresistance: A promising therapeutic target in radiotherapy
Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orbital Diseases and Ocular Oncology, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, P.R. China.
# These authors contributed equally to this report.
Abstract
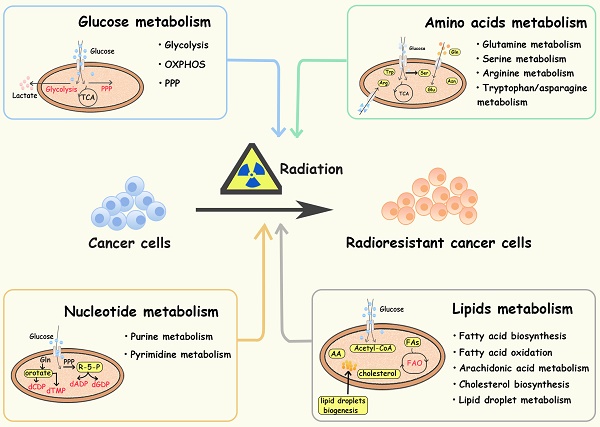
Currently, cancer treatment mainly consists of surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and molecular targeted therapy, of which radiotherapy is one of the major pillars. However, the occurrence of radioresistance largely limits its therapeutic effect. Metabolic reprogramming is an important hallmark in cancer progression and treatment resistance. In radiotherapy, DNA breakage is the major mechanism of cell damage, and in turn, cancer cells are prone to increase the metabolic flux of glucose, glutamine, serine, arginine, fatty acids etc., thus providing sufficient substrates and energy for DNA damage repair. Therefore, studying the linkage between metabolic reprogramming and cancer radioresistance may provide new ideas for improving the efficacy of tumor therapy. This review mainly focuses on the role of metabolic alterations, including glucose, amino acid, lipid, nucleotide and other ion metabolism, in radioresistance, and proposes possible therapeutic targets to improve the efficacy of cancer radiotherapy.
Keywords: Cancer, Radioresistance, Metabolic Reprogrammming, Therapeutic Targets

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact