10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2630-2647. doi:10.7150/ijbs.80743 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dendropanoxide Alleviates Thioacetamide-induced Hepatic Fibrosis via Inhibition of ROS Production and Inflammation in BALB/C Mice
1. School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, 2066, Seobu-ro, Jangan-gu, Suwon 440-746, Republic of Korea.
2. McLaughlin Centre for Population Health Risk Assessment, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
3. College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, 99 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon 34134, Republic of Korea.
4. School of Medical Sciences, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden; Cardiovascular Research Centre (CVRC), School of Medical Sciences, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden.
Abstract
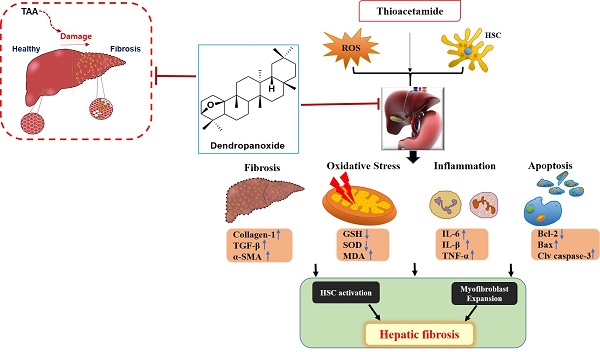
Hepatic fibrosis results from overproduction and excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in hepatocytes. Although the beneficial effects of dendropanoxide (DPx) isolated from Dendropanax morbifera have been studied, its role as an anti-fibrotic agent remains elucidated. We investigated the protective effect of DPx in BALB/C mice that received thioacetamide (TAA) intraperitoneally for 6 weeks. Later DPx (20 mg/kg/day) or silymarin (50 mg/kg/day) was administered daily for 6 weeks, followed by biochemical and histological analyses of each group. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the livers showed TAA-induced hepatic fibrosis, which was significantly reduced in the DPx group. DPx treatment significantly decreased TAA-induced hyperlipidemia as evidenced by the decreased AST, ALT, ALP, γ-GTP and serum TG concentrations and reduced the activities of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. ELISA revealed reduced levels of total glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA) and Inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α). Immunostaining showed reduced in collagen-1, α-SMA, and TGF-β1 expression and western blotting showed reduced levels of the apoptotic proteins, TGF-β1, p-Smad2/3, and Smad4. RT-qPCR and Western blotting revealed modifications in SIRT1, SIRT3 and SIRT4. Thus, DPx exerted a protective effect against TAA-induced hepatic fibrosis in the male BALB/C mouse model by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via TGF-β1/Smads signaling.
Keywords: Hepatic fibrosis, Thioacetamide, Oxidative stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis, Dendropanoxide

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact