10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2725-2739. doi:10.7150/ijbs.78588 This issue Cite
Research Paper
EIF4a3-regulated circRABL2B regulates cell stemness and drug sensitivity of lung cancer via YBX1-dependent downregulation of MUC5AC expression
1. The State Key Lab of Respiratory Disease, Institute of Public Health, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China.
2. Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Guangzhou First People's Hospital, the Second Affiliated Hospital of South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510080, China.
3. Innovation center for Advanced Interdisciplinary Medicine, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510735, China.
4. The State Key Lab of Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China.
# Liming Lu, Yuyuan Zeng, Ziqi Yu, and Shizhen Chen contributed equally.
Abstract
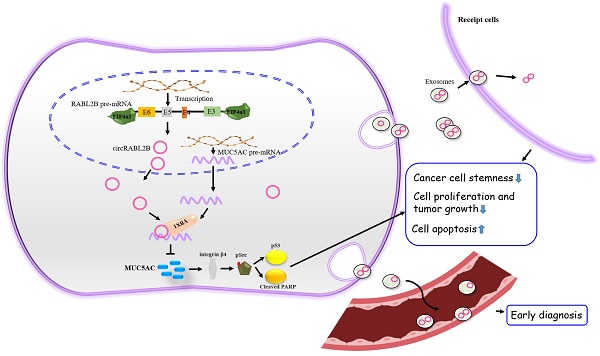
Identification of mucin modulators is of remarkable significance to facilitate mucin-based antineoplastic therapy. However, little is known about circular RNAs (circRNAs) on regulating mucins. Dysregulated mucins and circRNAs were identified via high-throughput sequencing and their relationships with lung cancer survival were analyzed in tumor samples of 141 patients. The biological functions of circRABL2B were determined via gain- and loss-of-function experiments and exosome-packaged circRABL2B treatment in cells, patient-derived lung cancer organoids and nude mice. We identified that circRABL2B was negatively correlated with MUC5AC. Patients with low circRABL2B and high MUC5AC displayed the poorest survival (HR=2.00; 95% CI=1.12-3.57). Overexpressed circRABL2B significantly inhibited cell malignant phenotypes, while it knock-down exerted opposite effects. CircRABL2B interacted with YBX1 to inhibit MUC5AC, and subsequently suppressed integrin β4/pSrc/p53 signaling and impoverished cell stemness, and promoted erlotinib sensitivity. Exosome-packaged circRABL2B exerted significant anti-cancer actions in cells, patient-derived lung cancer organoids and nude mice. Meanwhile, circRABL2B in plasma exosomes could distinguish early-stage lung cancer patients from healthy controls. Finally, we found circRABL2B was downregulated at the transcriptional level, and EIF4a3 involved the formation of circRABL2B. In conclusion, our data suggest that circRABL2B counteracts lung cancer progression via MUC5AC/integrin β4/pSrc/p53 axis, which provides a rationale to enhance the efficacy of anti-MUCs treatment in lung cancer.
Keywords: mucins, circRABL2B, lung cancer, exosomes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact