10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2740-2755. doi:10.7150/ijbs.83024 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Upregulated desmin/integrin β1/MAPK axis promotes elastic cartilage regeneration with increased ECM mechanical strength
Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100144, PR China.
† These authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Abstract
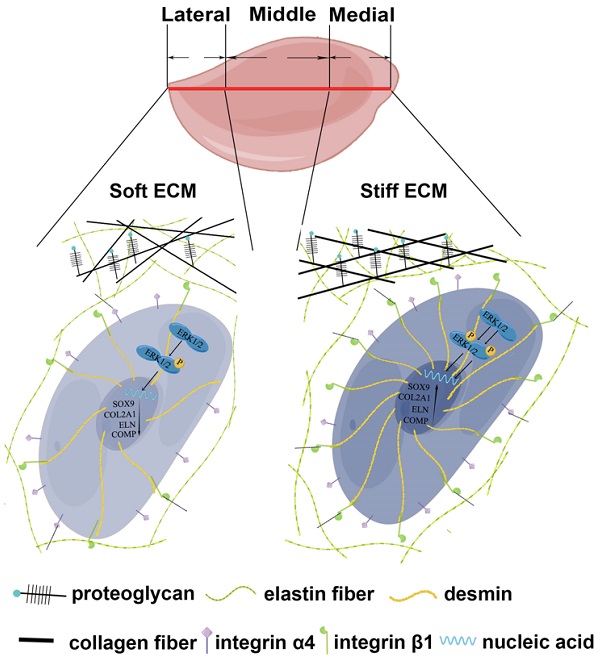
Elastic cartilage tissue engineering is promising for providing available scaffolds for plastic reconstructive surgery. The insufficient mechanical strength of regenerative tissue and scarce resources of reparative cells are two obstacles for the preparation of tissue-engineered elastic cartilage scaffolds. Auricular chondrocytes are important reparative cells for elastic cartilage tissue engineering, but resources are scarce. Identifying auricular chondrocytes with enhanced capability of elastic cartilage formation is conducive to reducing the damage to donor sites by decreasing the demand on native tissue isolation. Based on the biochemical and biomechanical differences in native auricular cartilage, we found that auricular chondrocytes with upregulated desmin expressed more integrin β1, forming a stronger interaction with the substrate. Meanwhile, activated MAPK pathway was found in auricular chondrocytes highly expressing desmin. When desmin was knocked down, the chondrogenesis and mechanical sensitivity of chondrocytes were both impaired, and the MAPK pathway was downregulated. Finally, auricular chondrocytes highly expressing desmin regenerated more elastic cartilage with increased ECM mechanical strength. Therefore, desmin/integrin β1/MAPK signaling can not only serve as a selection standard but also a manipulation target of auricular chondrocytes to promote elastic cartilage regeneration.
Keywords: auricular chondrocyte, tissue engineering, desmin, integrin β1, MAPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact