10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2897-2913. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81210 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TLR9 and STING agonists cooperatively boost the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 RBD vaccine through an increased germinal center B cell response and reshaped T helper responses
1. Immunology Research Center, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan.
2. National Institute of Infectious Diseases and Vaccinology, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan.
3. Institute of Molecular Medicine, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
4. Graduate Institute of Immunology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
5. Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Nanomedicine, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan.
6. Department of Life Sciences, National Central University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
7. Program in Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Abstract
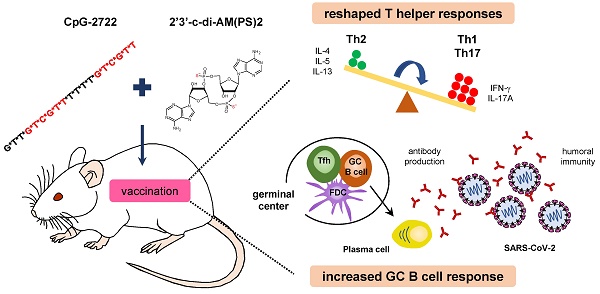
Vaccines are a powerful medical intervention for preventing epidemic diseases. Efficient inactivated or protein vaccines typically rely on an effective adjuvant to elicit an immune response and boost vaccine activity. In this study, we investigated the adjuvant activities of combinations of Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonists in a SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain protein vaccine. Adjuvants formulated with a TLR9 agonist, CpG-2722, with various cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) that are STING agonists increased germinal center B cell response and elicited humoral immune responses in immunized mice. An adjuvant containing CpG-2722 and 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 effectively boosted the immune response to both intramuscularly and intranasally administrated vaccines. Vaccines adjuvanted with CpG-2722 or 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 alone were capable of inducing an immune response, but a cooperative adjuvant effect was observed when both were combined. CpG-2722 induced antigen-dependent T helper (Th)1 and Th17 responses, while 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 induced a Th2 response. The combination of CpG-2722 and 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 generated a distinct antigen-dependent Th response profile characterized by higher Th1 and Th17, but lower Th2 responses. In dendritic cells, CpG-2722 and 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 showed a cooperative effect on inducing expression of molecules critical for T cell activation. CpG-2722 and 2'3'-c-di-AM(PS)2 have distinct cytokine inducing profiles in different cell populations. The combination of these two agonists enhanced the expression of cytokines for Th1 and Th17 responses and suppressed the expression of cytokines for Th2 response in these cells. Thus, the antigen-dependent Th responses observed in the animals immunized with different vaccines were shaped by the antigen-independent cytokine-inducing profiles of their adjuvant. The expanded targeting cell populations, the increased germinal center B cell response, and reshaped T helper responses are the molecular bases for the cooperative adjuvant effect of the combination of TLR9 and STING agonists.
Keywords: Adjuvant, CpG-oligodeoxynucleotide, Cyclic dinucleotide, SARS-CoV-2, Stimulator of interferon genes, Toll-like receptor, Vaccine.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact