10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(13):4278-4290. doi:10.7150/ijbs.87763 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Radioimmunotherapy Targeting B7-H3 in situ glioma models enhanced antitumor efficacy by Reconstructing the tumor microenvironment
1. Department of Clinical Pharmacology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, SZ, China.
2. Institute for Interdisciplinary Drug Research and Translational Sciences, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, Suzhou, SZ, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Soochow University, Suzhou, SZ, China.
4. Jiangsu Institute of Clinical Immunology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, SZ, China.
5. SuZhou Bright Scistar Antibody Biotech co., Ltd, 303-305, Bldg 15, NO.8, Jinfeng Road, Suzhou, SZ, China.
* Co-first authors
Abstract
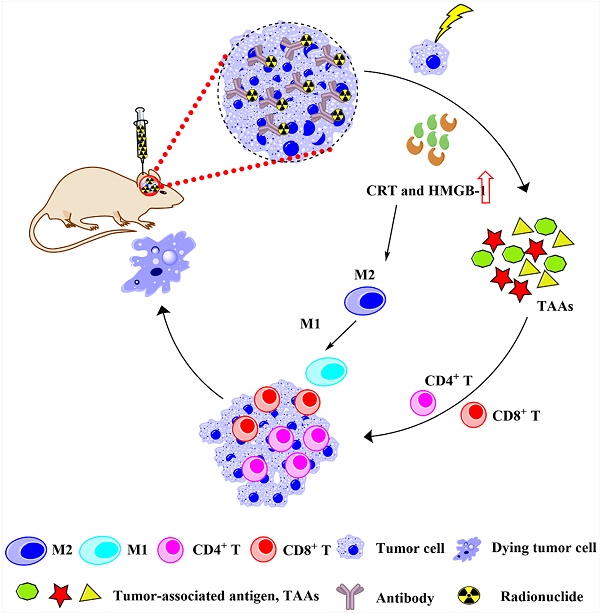
Radionuclide drug conjugates (RDCs) with antibodies serve as a novel approach for the treatment of malignant tumors including glioblastoma. However, RDCs require optimal antibodies to work efficiently. Hu4G4, a novel B7-H3-targeting humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody, is highly specific for the human B7-H3 protein (a marker of tumor cells, including glioblastoma cells). Herein, we established 131I-labeled hu4G4 (131I-hu4G4) and showed that it specifically bound to B7-H3 with high affinity (Kd = 0.99 ± 0.07 nM) and inhibited the growth of U87 cells in vitro. 131I-hu4G4 displayed potent in situ antitumor activity in a mouse model of glioma based on GL261 Red-Fluc-B7-H3 cells. More importantly, 131I-hu4G4 remodeled the tumor microenvironment and promoted the transformation of glioma from “cold” to “hot” tumors by promoting CD4+ and CD8+ T cell infiltration and the polarization of M2 to M1. Therefore, the antitumor activity observed with 131I-hu4G4, together with its ability to enhance antitumor immune responses, makes it a novel candidate for radioimmunotherapy of glioblastoma.
Keywords: B7-H3, radionuclide drug conjugate, glioblastoma, pharmacodynamics, tumor microenvironment.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact