10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(16):5074-5088. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84472 This issue Cite
Research Paper
S100a16 Deficiency Prevents Alcohol-induced Fatty Liver Injury via Inducing MANF Expression in Mice
1. Department of Geriatrics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China.
2. Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China.
3. Department of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China.
4. Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China.
5. Department of Medical Informatics, School of Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
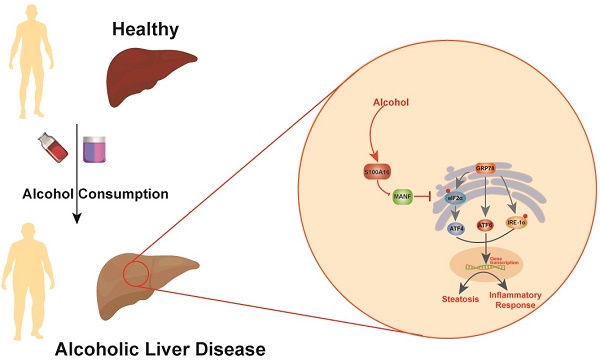
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) encompasses conditions ranging from simple steatosis to cirrhosis and even liver cancer. It has gained significant global attention in recent years. Despite this, effective pharmacological treatments for ALD remain elusive, and the core mechanisms underlying the disease are not yet fully comprehended. S100A16, a newly identified calcium-binding protein, is linked to lipid metabolism. Our research has discovered elevated levels of the S100A16 protein in both serum and liver tissue of ALD patients. A similar surge in hepatic S100A16 expression was noted in a Gao-binge alcohol feeding mouse model. S100a16 knockdown alleviated ethanol-induced liver injury, steatosis and inflammation. Conversely, S100a16 transgenic mice showed aggravating phenomenon. Mechanistically, we identify mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) as a regulated entity downstream of S100a16 deletion. MANF inhibited ER-stress signal transduction induced by alcohol stimulation. Meanwhile, MANF silencing suppressed the inhibition effect of S100a16 knockout on ethanol-induced lipid droplets accumulation in primary hepatocytes. Our data suggested that S100a16 deletion protects mice against alcoholic liver lipid accumulation and inflammation dependent on upregulating MANF and inhibiting ER stress. This offers a potential therapeutic avenue for ALD treatment.
Keywords: Alcoholic liver disease, S100A16, hepatic steatosis, MANF, ER stress.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact