ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):1-14. doi:10.7150/ijbs.88285 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MRCK as a Potential Target for Claudin-Low Subtype of Breast Cancer
1. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung City 406040, Taiwan R.O.C.
2. Center for Molecular Medicine, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung City 40402, Taiwan R.O.C.
3. Research Center for Cancer Biology, China Medical University, Taichung City 40402, Taiwan R.O.C.
4. Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
5. Bristol-Myers Squibb, Redwood City, CA 94063, USA.
* These authors are equally contributed.
Abstract
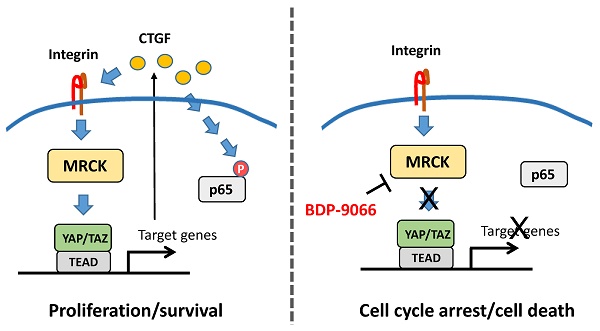
To find new molecular targets for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), we analyzed a large-scale drug screening dataset based on breast cancer subtypes. We discovered that BDP-9066, a specific MRCK inhibitor (MRCKi), may be an effective drug against TNBC. After confirming the efficacy and specificity of BDP-9066 against TNBC in vitro and in vivo, we further analyzed the underlying mechanism of specific activity of BDP-9066 against TNBC. Comparing the transcriptome of BDP-9066-sensitive and -resistant cells, the activation of the focal adhesion and YAP/TAZ pathway were found to play an important role in the sensitive cells. Furthermore, YAP/TAZ is indeed repressed by BDP-9066 in the sensitive cells, and active form of YAP suppresses the effects of BDP-9066. YAP/TAZ expression and activity are high in TNBC, especially the Claudin-low subtype, consistent with the expression of focal adhesion-related genes. Interestingly, NF-κB functions downstream of YAP/TAZ in TNBC cells and is suppressed by BDP-9066. Furthermore, the PI3 kinase pathway adversely affected the effects of BDP-9066 and that alpelisib, a PI3 kinase inhibitor, synergistically increased the effects of BDP-9066, in PIK3CA mutant TNBC cells. Taken together, we have shown for the first time that MRCKi can be new drugs against TNBC, particularly the Claudin-low subtype.
Keywords: TNBC, Claudin-low, MRCK, YAP/TAZ, Focal adhesions, p65

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact