10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):113-126. doi:10.7150/ijbs.87305 This issue Cite
Review
The Role of Nuclear Receptors in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
1. Hepatic Surgery Center, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China.
2. Clinical Medicine Research Center for Hepatic Surgery of Hubei Province, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China.
3. Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College and State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Severe Zoonostic Infectious Disease, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China.
Abstract
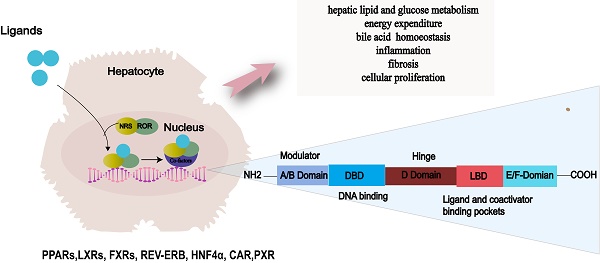
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a global health burden closely linked to insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. The complex pathophysiology of NAFLD involves multiple cellular pathways and molecular factors. Nuclear receptors (NRs) have emerged as crucial regulators of lipid metabolism and inflammation in NAFLD, offering potential therapeutic targets for NAFLD. Targeting PPARs and FXRs has shown promise in ameliorating NAFLD symptoms and halting disease progression. However, further investigation is needed to address side effects and personalize therapy approaches. This review summarizes the current understanding of the involvement of NRs in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and explores their therapeutic potential. We discuss the role of several NRs in modulating lipid homeostasis in the liver, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), liver X receptors (LXRs), farnesoid X receptors (FXRs), REV-ERB, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and pregnane X receptor (PXR).The expanding knowledge of NRs in NAFLD offers new avenues for targeted therapies, necessitating exploration of novel treatment strategies and optimization of existing approaches to combat this increasingly prevalent disease.
Keywords: NAFLD, NRs, PPARs, FXR, LXR

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact