ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):152-174. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84890 This issue Cite
Review
The Role of cGAS-STING Signalling in Metabolic Diseases: from Signalling Networks to Targeted Intervention
1. College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Functional Dairy, Department of Nutrition and Health, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China.
3. Hebei Engineering Research Center of Animal Product, Sanhe 065200, China.
4. Inner Mongolia Mengniu Dairy (Group) Co., Ltd., Hohhot 011517, China.
5. Research Center for Probiotics, China Agricultural University, Sanhe 065200, China.
6. Food Laboratory of Zhongyuan, Luohe 462300, China.
Abstract
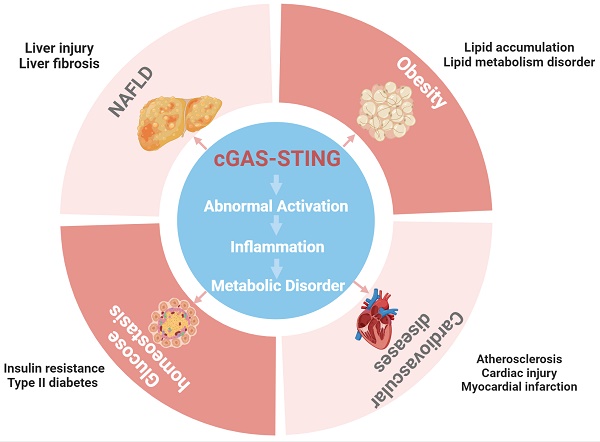
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a crucial innate defence mechanism against viral infection in the innate immune system, as it principally induces the production of type I interferons. Immune responses and metabolic control are inextricably linked, and chronic low-grade inflammation promotes the development of metabolic diseases. The cGAS-STING pathway activated by double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs), endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress), mitochondrial stress, and energy imbalance in metabolic cells and immune cells triggers proinflammatory responses and metabolic disorders. Abnormal overactivation of the pathway is closely associated with metabolic diseases such as obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The interaction of cGAS-STING with other pathways, such as the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), autophagy, pyroptosis and insulin signalling pathways, is considered an important mechanism by which cGAS-STING regulates inflammation and metabolism. This review focuses on the link between immune responses related to the cGAS-STING pathway and metabolic diseases and cGAS-STING interaction with other pathways for mediating signal input and affecting output. Moreover, potential inhibitors of the cGAS-STING pathway and therapeutic prospects against metabolic diseases are discussed. This review provides a comprehensive perspective on the involvement of STING in immune-related metabolic diseases.
Keywords: cGAS, STING, metabolic diseases, inflammation, signalling network, target intervention

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact