10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):182-199. doi:10.7150/ijbs.87180 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TRAF4 regulates ubiquitination-modulated survivin turnover and confers radioresistance
1. Department of Radiology, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China.
2. Cell Transplantation and Gene Therapy Institute, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China.
3. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China.
4. Hunan Provincial People's Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University, Changsha, Hunan, 410005, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
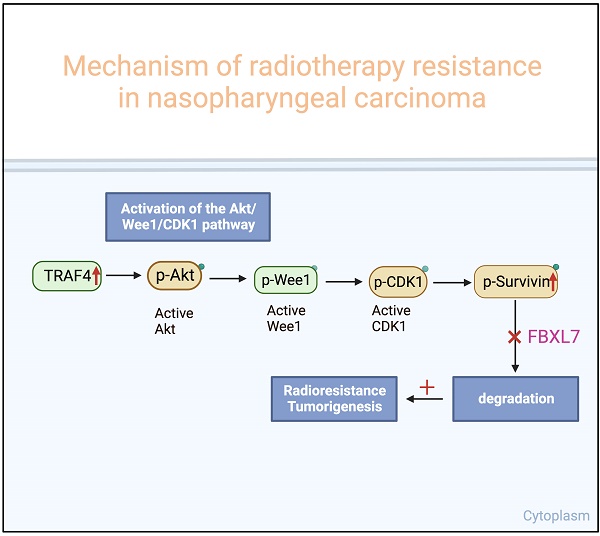
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx. Despite continuous improvement in treatment strategies, recurrence or persistence of cancer after radiotherapy is still inevitable, highlighting the need to identify therapeutic resistance factors and develop effective methods for NPC treatment. Herein, we found that TRAF4 is overexpressed in NPC cells and tissues. Knockdown TRAF4 significantly increased the radiosensitivity of NPC cells, possibly by inhibiting the Akt/Wee1/CDK1 axis, thereby suppressing survivin phosphorylation and promoting its degradation by FBXL7. TRAF4 is positively correlated with p-Akt and survivin in NPC tissues. High protein levels of TRAF4 were observed in acquired radioresistant NPC cells, and knockdown of TRAF4 overcomes radioresistant in vitro and the xenograft mouse model. Altogether, our study highlights the TRAF4-survivin axis as a potential therapeutic target for radiosensitization in NPC.
Keywords: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, TRAF4, Survivin, Radioresistance, Ubiquitination

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact