ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):231-248. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86317 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-driven TNS4 fosters HNSCC tumorigenesis by stabilizing integrin α5β1 complex and triggering FAK-mediated Akt and TGFβ signaling pathways
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, 210029, China.
2. Stomatological Hospital, School of Stomatology, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510280, China.
Abstract
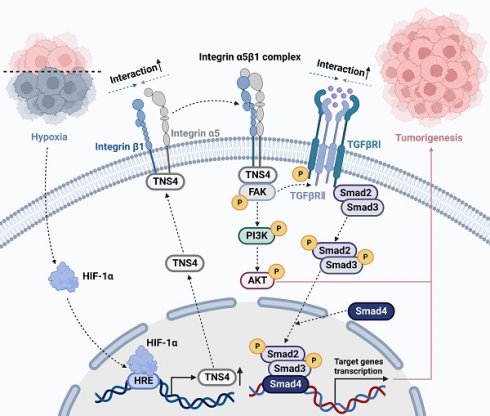
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains a formidable clinical challenge due to its high recurrence rate and limited targeted therapeutic options. This study aims to elucidate the role of tensin 4 (TNS4) in the pathogenesis of HNSCC across clinical, cellular, and animal levels. We found a significant upregulation of TNS4 expression in HNSCC tissues compared to normal controls. Elevated levels of TNS4 were associated with adverse clinical outcomes, including diminished overall survival. Functional assays revealed that TNS4 knockdown attenuated, and its overexpression augmented, the oncogenic capabilities of HNSCC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistic studies revealed that TNS4 overexpression promotes the interaction between integrin α5 and integrin β1, thereby activating focal adhesion kinase (FAK). This TNS4-mediated FAK activation simultaneously enhanced the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and facilitated the interaction between TGFβRI and TGFβRII, leading to the activation of the TGFβ signaling pathway. Both of these activated pathways contributed to HNSCC tumorigenesis. Additionally, we found that hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) transcriptionally regulated TNS4 expression. In conclusion, our findings provide the basis for innovative TNS4-targeted therapeutic strategies, which could potentially improve prognosis and survival rates for patients with HNSCC.
Keywords: tensin 4, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, integrin α5β1, HIF-1α, TGF-β

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact