ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):347-366. doi:10.7150/ijbs.88500 This issue Cite
Review
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy Resistance: from Biology to Clinical Opportunity
1. Institute of Translational Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, College of Medicine, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266021, China.
2. Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266021, China.
Abstract
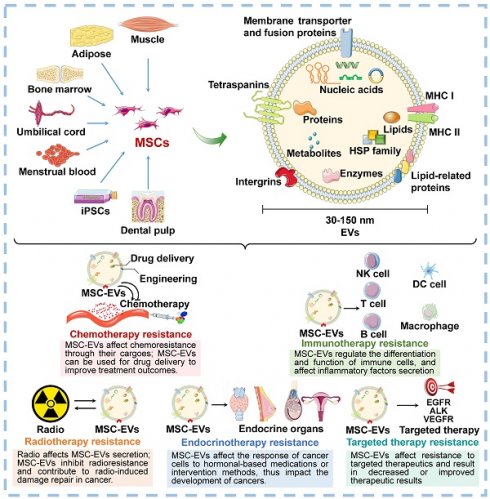
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of stromal cells characterized by their properties of self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation, which make them prominent in regenerative medicine. MSCs have shown significant potential for the treatment of various diseases, primarily through the paracrine effects mediated by soluble factors, specifically extracellular vesicles (EVs). MSC-EVs play a crucial role in intercellular communication by transferring various bioactive substances, including proteins, RNA, DNA, and lipids, highlighting the contribution of MSC-EVs in regulating cancer development and progression. Remarkably, increasing evidence indicates the association between MSC-EVs and resistance to various types of cancer treatments, including radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and endocrinotherapy. In this review, we provide an overview of the recent advancements in the biogenesis, isolation, and characterization of MSC-EVs, with an emphasis on their functions in cancer therapy resistance. The clinical applications and future prospects of MSC-EVs for mitigating cancer therapy resistance and enhancing drug delivery are also discussed. Elucidating the role and mechanism of MSC-EVs in the development of treatment resistance in cancer, as well as evaluating the clinical significance of MSC-EVs, is crucial for advancing our understanding of tumor biology. Meanwhile, inform the development of effective treatment strategies for cancer patients in the future.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cell, extracellular vesicle, cancer, therapy resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact