10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(4):1471-1491. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86719 This issue Cite
Research Paper
METTL16 suppressed the proliferation and cisplatin-chemoresistance of bladder cancer by degrading PMEPA1 mRNA in a m6A manner through autophagy pathway
1. Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China.
2. Laboratory of Urology and Andrology, Jiangsu Clinical Medicine Research Institution, Nanjing 210029, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
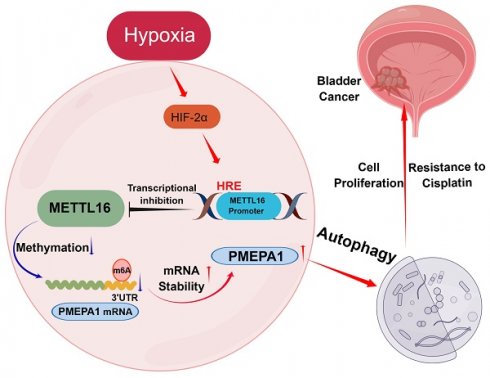
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is important in the physiological processes of many species. Methyltransferase-like 16 (METTL16) is a novel discovered m6A methylase, regulating various tumors in an m6A-dependent manner. However, its function in bladder cancer (BLCA) remains largely unclear. In the present study, we found that low expression of METTL16 predicted poor survival in BLCA patients. METTL16 inhibited the proliferation and cisplatin-resistance function of bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. In addition, METTL16 reduced the mRNA stability of prostate transmembrane protein androgen induced-1 (PMEPA1) via binding to its m6A site in the 3'-UTR, thereby inhibited the proliferation of bladder cancer cells and increased the sensitivity of cisplatin through PMEPA1-mediated autophagy pathway. Finally, we found that hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) exerted its tumor-promoting effect by binding the METTL16 promoter region to repress its transcription. Taken together, High expression of METTL16 predicted better survival in BLCA. METTL16 significantly inhibited bladder cancer cell proliferation and sensitized bladder cancer cells to cisplatin via HIF-2α-METTL16-PMEPA1-autophagy axis in a m6A manner. These findings might provide fresh insights into BLCA therapy.
Keywords: METTL16, bladder cancer, PMEPA1, autophagy, HIF-2α

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact