10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(5):1669-1687. doi:10.7150/ijbs.90872 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tubule-specific cyclin-dependent kinase 12 knockdown potentiates kidney injury through transcriptional elongation defects
1. Institute of Nephrology, Zhong Da Hospital, Southeast University School of Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
2. Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
3. Department of Nephrology, The Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China.
4. Shanghai OE Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
5. Institute of Nephrology, The Affiliated Taizhou People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Taizhou School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jinagsu, China.
6. Department of Pediatric Nephrology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
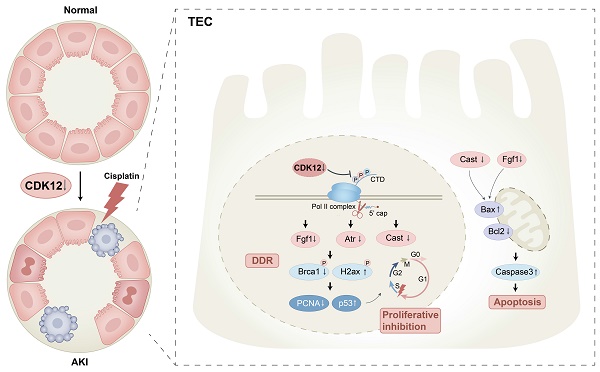
Direct tubular injury caused by several medications, especially chemotherapeutic drugs, is a common cause of AKI. Inhibition or loss of cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12) triggers a transcriptional elongation defect that results in deficiencies in DNA damage repair, producing genomic instability in a variety of cancers. Notably, 10-25% of individuals developed AKI after treatment with a CDK12 inhibitor, and the potential mechanism is not well understood. Here, we found that CDK12 was downregulated in the renal tubular epithelial cells in both patients with AKI and murine AKI models. Moreover, tubular cell-specific knockdown of CDK12 in mice enhanced cisplatin-induced AKI through promotion of genome instability, apoptosis, and proliferative inhibition, whereas CDK12 overexpression protected against AKI. Using the single molecule real-time (SMRT) platform on the kidneys of CDK12RTEC+/- mice, we found that CDK12 knockdown targeted Fgf1 and Cast through transcriptional elongation defects, thereby enhancing genome instability and apoptosis. Overall, these data demonstrated that CDK12 knockdown could potentiate the development of AKI by altering the transcriptional elongation defect of the Fgf1 and Cast genes, and more attention should be given to patients treated with CDK12 inhibitors to prevent AKI.
Keywords: CDK12, Apoptosis, DNA damage, AKI, Proximal tubule, Transcriptional elongation defect, Fgf1, Cast

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact