ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(5):508-524. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11241 This issue Cite
Review
Modulation of Glucose Transporter Protein by Dietary Flavonoids in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
1. Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia;
2. Faculty of Pharmacy, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), 42300 Bandar Puncak Alam, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia.
* These authors had equal contribution in this work.
Abstract
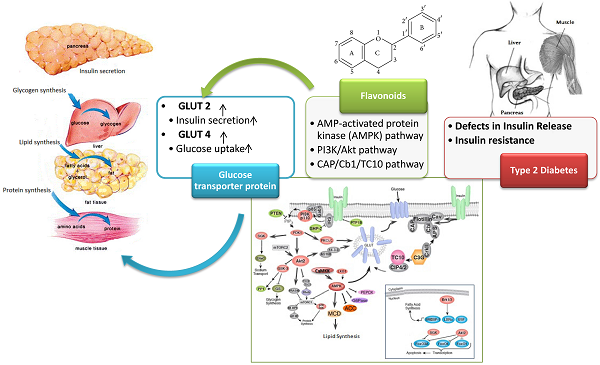
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia due to insufficient or inefficient insulin secretory response. This chronic disease is a global problem and there is a need for greater emphasis on therapeutic strategies in the health system. Phytochemicals such as flavonoids have recently attracted attention as source materials for the development of new antidiabetic drugs or alternative therapy for the management of diabetes and its related complications. The antidiabetic potential of flavonoids are mainly through their modulatory effects on glucose transporter by enhancing GLUT-2 expression in pancreatic β cells and increasing expression and promoting translocation of GLUT-4 via PI3K/AKT, CAP/Cb1/TC10 and AMPK pathways. This review highlights the recent findings on beneficial effects of flavonoids in the management of diabetes with particular emphasis on the investigations that explore the role of these compounds in modulating glucose transporter proteins at cellular and molecular level.
Keywords: Glucose transporter protein, insulin, type 2 diabetes mellitus, flavonoids, glucose uptake.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact