10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(5):536-545. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10754 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Regulates TRPC3/6 Channels and Protects Against Myocardial Infarction in Rodents
1. Institute of Clinical Pharmacology of the Second Affiliated Hospital (Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Heilongjiang Higher Education Institutions), Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, China.
2. Department of Cardiology of the First Affiliated Hospital (Key Laboratory of Cardiac Diseases and Heart Failure), Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, China.
3. Department of Pharmacology (State-Province Key Laboratories of Biomedicine- Pharmaceutics of China, Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Research, Ministry of Education), Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150081, China.
# The first two authors made equal contribution to this research.
Abstract
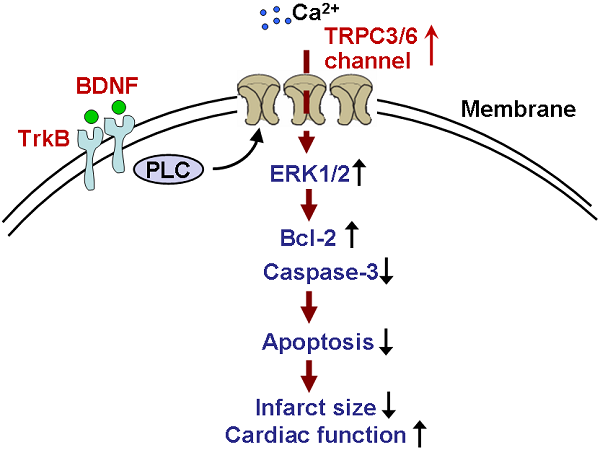
Background: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is associated with coronary artery diseases. However, its role and mechanism in myocardial infarction (MI) is not fully understood.
Methods: Wistar rat and Kunming mouse model of MI were induced by the ligation of left coronary artery. Blood samples were collected from MI rats and patients. Plasma BDNF level, protein expression of BDNF, tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) and its downstream transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)3/6 channels were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blot. Infarct size, cardiac function and cardiomyocyte apoptosis were measured after intra-myocardium injection with recombinant human BDNF. Protective role of BDNF against cardiomyocyte apoptosis was confirmed by BDNF scavenger TrkB-Fc. The regulation of TRPC3/6 channels by BDNF was validated by pretreating with TRPC blocker (2-Aminoethyl diphenylborinate, 2-APB) and TRPC3/6 siRNAs.
Results: Circulating BDNF was significantly enhanced in MI rats and patients. Protein expression of BDNF, TrkB and TRPC3/6 channels were upregulated in MI. 3 days post-MI, BDNF treatment markedly reduced the infarct size and serum lactate dehydrogenase activity. Meanwhile, echocardiography indicated that BDNF significantly improved cardiac function of MI mice. Furthermore, BDNF markedly inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis by upregulating Bcl-2 expression and downregulating caspase-3 expression and activity in ischemic myocardium. In neonatal rat ventricular myocytes, cell viability was dramatically increased by BDNF in hypoxia, which was restored by TrkB-Fc. Furthermore, protective role of BDNF against hypoxia-induced apoptosis was reversed by 2-APB and TRPC3/6 siRNAs.
Conclusion: BDNF/TrkB alleviated cardiac ischemic injury and inhibited cardiomyocytes apoptosis by regulating TRPC3/6 channels, which provides a novel potential therapeutic candidate for MI.
Keywords: Brain derived neurotrophic factor, Myocardial infarction, Transient receptor potential canonical channel, Apoptosis, TrkB-Fc

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact