10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(5):559-568. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10690 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ER Stress and Autophagy Dysfunction Contribute to Fatty Liver in Diabetic Mice
1. Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical College, Guiyang, Guizhou, China, 550004
2. Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY 40202, USA
3. Chinese-American Research Institute for Diabetic Complications RuiAn Center, the Department of Endocrinology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Ruian, Zhejiang, China, 325200
4. Kosair Children's Hospital Research Institute, the Department of Pediatrics of the University of Louisville, Louisville, KY 40202, USA
5. The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China 130021
Abstract
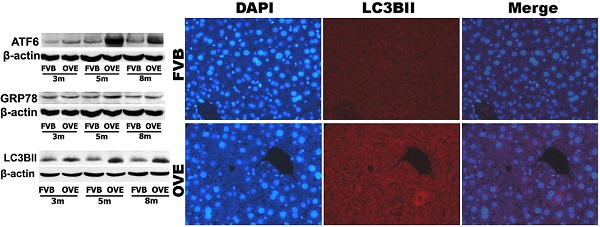
Diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are often identified in patients simultaneously. Recent evidence suggests that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy dysfunction play an important role in hepatocytes injury and hepatic lipid metabolism, however the mechanistic interaction between diabetes and NAFLD is largely unknown. In this study, we used a diabetic mouse model to study the interplay between ER stress and autophagy during the pathogenic transformation of NAFLD. The coexist of inflammatory hepatic injury and hepatic accumulation of triglycerides (TGs) stored in lipid droplets indicated development of steatohepatitis in the diabetic mice. The alterations of components for ER stress signaling including ATF6, GRP78, CHOP and caspase12 indicated increased ER stress in liver tissues in early stage but blunted in the later stage during the development of diabetes. Likewise, autophagy functioned well in the early stage but suppressed in the later stage. The inactivation of unfolded protein response and suppression of autophagy were positively related to the development of steatohepatitis, which linked to metabolic abnormalities in the compromised hepatic tissues in diabetic condition. We conclude that the adaption of ER stress and impairment of autophagy play an important role to exacerbate lipid metabolic disorder contributing to steatohepatitis in diabetes.
Keywords: Autophagic dysfunction, ER stress, Diabetes, Diabetic liver toxicity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact