10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(8):923-934. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10896 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sensitization of Chemo-Resistant Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem-Like Cells to Hsp90 Inhibitor by SIRT1 Inhibition
1. Department of Biochemistry, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan 626-870, Korea
2. Korea Mouse Metabolic Phenotyping Center, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, Gachon University, Incheon 406-840, Korea
3. College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-818, Korea
* These authors contributed equally to this study as corresponding authors.
Abstract
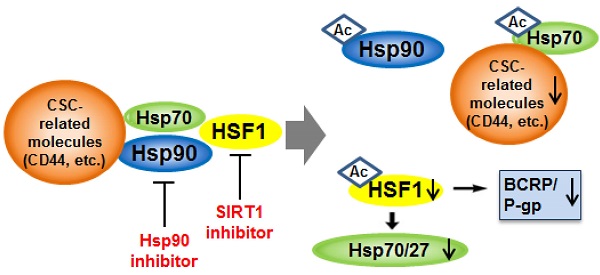
Development of effective therapeutic strategies to eliminate cancer stem-like cells (CSCs), which play a major role in drug resistance and disease recurrence, is critical to improve cancer treatment outcomes. The current investigation was undertaken to examine the effectiveness of the combination treatment of Hsp90 inhibitor and SIRT1 inhibitor in inhibiting the growth of chemo-resistant stem-like cells isolated from human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells. Inhibition of SIRT1 by use of SIRT1 siRNA or SIRT1 inhibitors (amurensin G and EX527) effectively potentiated sensitivity of Hsp90 inhibitors (17-AAG and AUY922) in CD44high K562 stem-like cells expressing high levels of CSC-related molecules including Oct4, CD34, β-catenin, c-Myc, mutant p53 (mut p53), BCRP and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) as well as CD44. SIRT1 depletion caused significant down-regulation of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1)/heat shock proteins (Hsps) as well as these CSC-related molecules, which led to the sensitization of CD44high K562 cells to Hsp90 inhibitor by SIRT1 inhibitor. Moreover, 17-AAG-mediated activation of HSF1/Hsps and P-gp-mediated efflux, major causes of Hsp90 inhibitor resistance, was suppressed by SIRT1 inhibitor in K562-CD44high cells. Our data suggest that combined treatment with Hsp90 inhibitor and SIRT1 inhibitor could be an effective therapeutic approach to target CSCs that are resistant to current therapies.
Keywords: Hsp90 inhibitor, K562, CD44, SIRT1 inhibitor, multidrug resistance, cancer stem-like cells

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact