10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(8):1000-1009. doi:10.7150/ijbs.13222 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Carbon Monoxide Improves Neurologic Outcomes by Mitochondrial Biogenesis after Global Cerebral Ischemia Induced by Cardiac Arrest in Rats
1. Department of Emergency Medicine, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
2. Institute of Cardiopulmonary Cerebral Resuscitation, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
3. Department of Emergency Medicine, The fifth affiliated hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, China
# These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
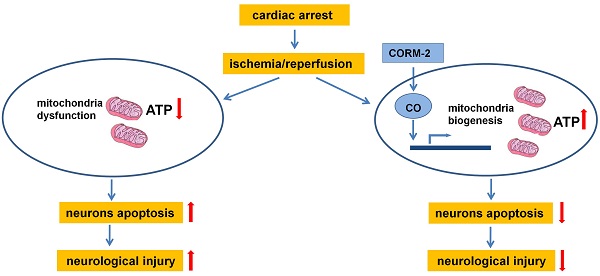
Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to brain injury following global cerebral ischemia after cardiac arrest. Carbon monoxide treatment has shown potent cytoprotective effects in ischemia/reperfusion injury. This study aimed to investigate the effects of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules on brain mitochondrial dysfunction and brain injury following resuscitation after cardiac arrest in rats. A rat model of cardiac arrest was established by asphyxia. The animals were randomly divided into the following 3 groups: cardiac arrest and resuscitation group, cardiac arrest and resuscitation plus carbon monoxide intervention group, and sham control group (no cardiac arrest). After the return of spontaneous circulation, neurologic deficit scores (NDS) and S-100B levels were significantly decreased at 24, 48, and 72 h, but carbon monoxide treatment improved the NDS and S-100B levels at 24 h and the 3-day survival rates of the rats. This treatment also decreased the number of damaged neurons in the hippocampus CA1 area and increased the brain mitochondrial activity. In addition, it increased mitochondrial biogenesis by increasing the expression of biogenesis factors including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α, nuclear respiratory factor-1, nuclear respiratory factor-2 and mitochondrial transcription factor A. Thus, this study showed that carbon monoxide treatment alleviated brain injury after cardiac arrest in rats by increased brain mitochondrial biogenesis.
Keywords: carbon monoxide, brain injury, cardiac arrest, mitochondria biogenesis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact