10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(10):1213-1224. doi:10.7150/ijbs.15496 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-628 Promotes Burn-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via Targeting IRS1
Department of Burn & Plastic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of PLA General Hospital, Beijing, 100048 China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
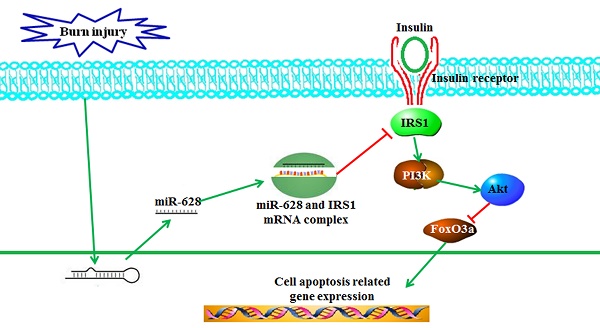
Skeletal muscle atrophy is a common clinical feature among patients with severe burns. Previous studies have shown that miRNAs play critical roles in the regulation of stress-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Our previous study showed that burn-induced skeletal muscle atrophy is mediated by miR-628. In this study, compared with sham rats, rats subjected to burn injury exhibited skeletal muscle atrophy, as well as significantly decreased insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) protein expression and significantly increased skeletal muscle cell apoptosis. An miRNA array showed that the levels of miR-628, a potential regulator of IRS1 protein translation, were also clearly elevated. Second, L6 myocyte cell apoptosis increased after induction of miR-628 expression, and IRS1 and p-Akt protein expression decreased significantly. Expression of the cell apoptosis-related proteins FoxO3a and cleaved caspase 3 also increased after induction of miR-628 expression. Finally, forced miR-628 expression in normal rats resulted in increased cell apoptosis and skeletal muscle atrophy, as well as changes in IRS1/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway activity consistent with the changes in protein expression described above. Inhibiting cell apoptosis with Z-VAD-FMK resulted in alleviation of burn-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. In general, our results indicate that miR-628 mediates burn-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating the IRS1/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway.
Keywords: miR-628, Burn, IRS1, Skeletal muscle atrophy.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact