10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(3):349-357. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16635 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of a novel human long non-coding RNA that regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by inhibiting SREBP-1c
1. MOH Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens, Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100076, P.R. China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100005, P.R. China;
3. Department of Microbiology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, Henan 453003, P.R. China.
Abstract
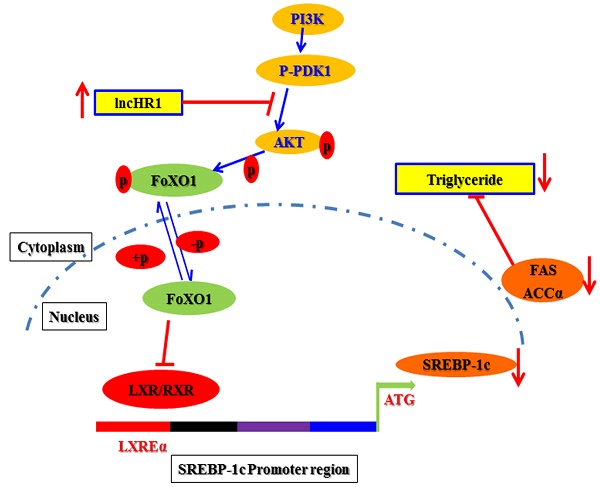
Sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) are master regulators of hepatic lipid homeostasis. Aberrant expression of SREBPs frequently leads to lipid metabolism dysregulation. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified with diverse biological functions, but the effects of lncRNAs on lipid metabolism are rarely reported. Here, we identified a novel human specific lncRNA, lncHR1, as a negative regulator of SREBP-1c expression. Overexpression of lncHR1 inhibited expression of SREBP-1c and fatty acid synthase (FAS) and then repressed oleic acid-induced hepatic cell triglyceride (TG) and lipid droplet (LD) accumulation. In vivo, the data of established transgenic animals showed that mice with lncHR1 expression had less hepatic expression of SREBP-1c, FAS, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase α (ACCα), and less hepatic and plasma TG after being fed a high-fat diet. Therefore, we report a novel lncRNA which can decrease lipid metabolism by repressing SREBP-1c gene expression.
Keywords: Long non-coding RNA, SREBP-1c, triglyceride, lipid metabolism.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact