10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(11):1409-1419. doi:10.7150/ijbs.21916 This issue Cite
Review
Altered Neuroendocrine Immune Responses, a Two-Sword Weapon against Traumatic Inflammation
State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burns and Combined Injury, Institute of Surgery Research, Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400042, China
Abstract
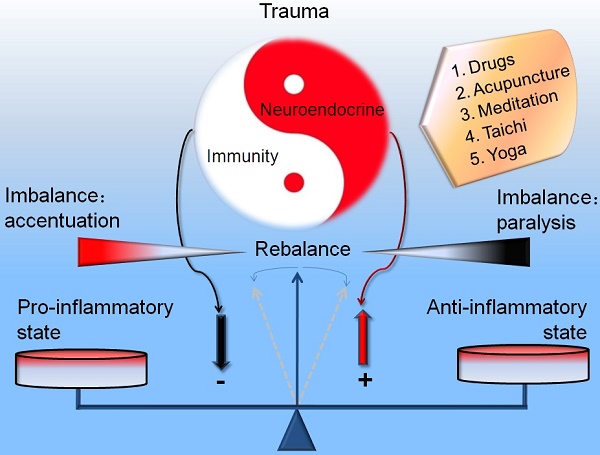
During the occurrence and development of injury (trauma, hemorrhagic shock, ischemia and hypoxia), the neuroendocrine and immune system act as a prominent navigation leader and possess an inter-system crosstalk between the reciprocal information dissemination. The fundamental reason that neuroendocrinology and immunology could mix each other and permeate toward the field of traumatology is owing to their same biological languages or chemical information molecules (hormones, neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, cytokines and their corresponding receptors) shared by the neuroendocrine and immune systems. The immune system is not only modulated by the neuroendocrine system, but also can modulate the biological functions of the neuroendocrine system. The interactive linkage of these three systems precipitates the complicated space-time patterns for the courses of traumatic inflammation. Recently, compelling evidence indicates that the network linkage pattern that initiating agents of neuroendocrine responses, regulatory elements of immune cells and effecter targets for immune regulatory molecules arouse the resistance mechanism disorders, which supplies the beneficial enlightenment for the diagnosis and therapy of traumatic complications from the view of translational medicine. Here we review the alternative protective and detrimental roles as well as possible mechanisms of the neuroendocrine immune responses in traumatic inflammation.
Keywords: trauma and injury, stress, infection, hormones, neuroendocrine system, immunity, translational medicine.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact