ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(12):1489-1496. doi:10.7150/ijbs.21637 This issue Cite
Review
The Molecular Mechanisms of Regulation on USP2's Alternative Splicing and the Significance of Its Products
Department of Oncology, Shanghai 9th People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, 639 Zhi Zao Ju Rd, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
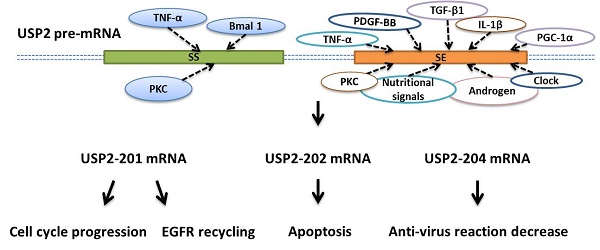
Ubiquitin-specific protease 2 (USP2) has a regulatory function in cell growth or death and is involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases. USP2 gene can generate 7 splicing variants through alternative splicing, and 5 variants respectively as USP2-201, USP2-202, USP2-204, USP2-205, USP2-206 can encode proteins. The influence of circadian rhythm, nutrition and androgen on specific signaling molecules or cytokines can regulate the alternative splicing of USP2. Specifically, PKC activator, IL-1β, TNF-α, PDGF-BB, TGF-β1 are all regulatory factors for USP2's alternative splicing. USP2-201 plays a crucial role in cell cycle progression, and is also of great significance in EGFR recycling. USP2-202 can activate apoptosis signaling pathway to participate in cell apoptosis, and USP2-204 can induce cell anti-virus reaction to decrease. In general, we collect and summarize the factors involved in the alternative splicing of USP2 in this review to further understand the mechanism behind the USP2's alternative splicing.
Keywords: USP2, alternative splicing, ubiquitin, deubiquitination, regulation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact