10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(7):791-798. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23744 This issue Cite
Review
Health risks associated with genetic alterations in internal clock system by external factors
1. The Key Laboratory of Aquatic Biodiversity and Conservation of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072, P.R China.
2. Henan Key Laboratory of Ecological Security for Water Source Region of Mid-line of South-to-North Diversion Project, Collaborative Innovation Center of Water Security for Water Source Region of Mid-line of South-to-North Diversion Project of Henan Province, Nanyang Normal University.
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049.
4. Advanced Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Center and Department of Biomedical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China.
5. Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources, Gansu Province / Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources Research, Institute of Geology and geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, 730000, China
Abstract
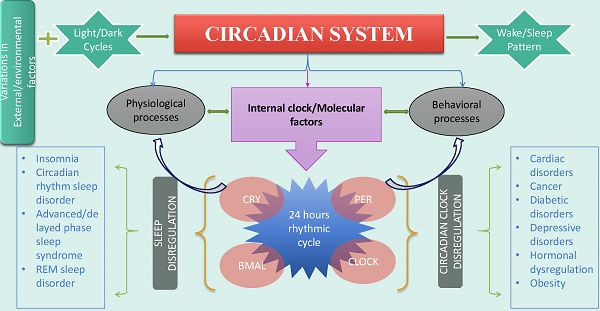
The circadian system maintains the main aspects of physiological and behavioral processes. Both circadian rhythm and sleep impact an organism's health through interaction with environmental factors. Variations in external factors influence the functionality of clock genes and disrupt 24-hour rhythmic cycle. The disrupted circadian rhythm and disregulated sleep affect an organism's health, thereby causing several disorders including cancer, depression and cardiac disorders. Considering the role of clock genes and environmental factors, extensive investigation is required focusing on pathways involved in development of life-threatening disorders. This review identifies the major risks and associated factors related with disruption in circadian system and sleep.
Keywords: Circadian system, sleep, health risks, clock genes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact