10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(1):208-220. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27537 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Establishing a prediction model for prostate cancer bone metastasis
1. Department of Urology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
2. Wuhan Clinical Cancer Research Center of Urology and Male Reproduction, Wuhan, China
3. Department of Biological Repositories, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
4. Human Genetics Resource Preservation Center of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
5. Medical Research Institute, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
6. Department of Urology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
7. Department of Pathology, Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University Medical School, Washington DC, USA
8. Department of Urology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA
*these authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
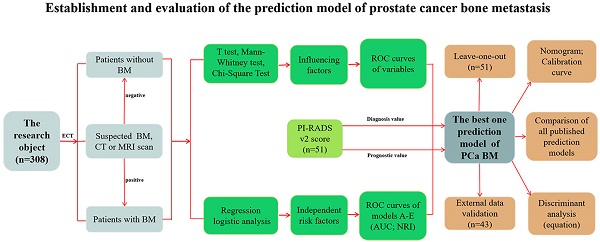
We collected clinical data from 308 prostate cancer (PCa) patients to investigate the clinical characteristics and independent risk factors of bone metastasis (BM) and to establish a prediction model for BM of PCa and determine the necessity of bone scans. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed based on age, biopsy Gleason score (BGS), clinical tumor stage (cTx), total prostate specific antigen (tPSA), free prostate specific antigen (fPSA), fPSA/tPSA, prostate volume, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), serum calcium and serum phosphorus. Moreover, 80 of the 308 PCa patients had a PI-RADS v2 score and were analysed retrospectively. The univariate analysis showed that the BGS, cTx, tPSA, fPSA, prostate volume and ALP were significant. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed significant differences among the BGS, cTx, tPSA and ALP. Four cases should be highly suspected with BM: (i) cTl-cT2, BGS ≤7, ALP >120 U/L and tPSA >90.64 ng/ml; (ii) cTl-cT2, BGS ≥8, and ALP >120 U/L; (iii) cT3-cT4, BGS ≤7, and ALP >120 U/L; and (iv) cT3-cT4 and BGS ≥8. After the PI-RADS v2 score was included in the model, the AUC of the prediction model rose from 0.884 (95% CI: 0.813-0.996) to 0.934 (95% CI: 0.883-0.986). This model may help determine the necessity of bone scans to diagnose BM for PCa patients.
Keywords: Prediction analysis model, prostate cancer, bone metastasis, PI-RADS v2, BGS, cTx, tPSA, ALP

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact