10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(3):568-578. doi:10.7150/ijbs.29759 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of Heme Oxygenase-1 enhances hyperthermia-induced autophagy and antiviral effect
1. Department of Dermatology, No.1 Hospital of China Medical University and Key Laboratory of Immunodermatology, Ministry of Health and Ministry of Education, Shenyang 110001, China
2. Department of Dermatology, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shen Yang Medical College, Shenyang, 110001, China
3. Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology, China Medical University, Shenyang, 110122, China
4. Department of Pathology, the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama 35249, United States
5. Department of Neurosurgery, No.1 Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
Abstract
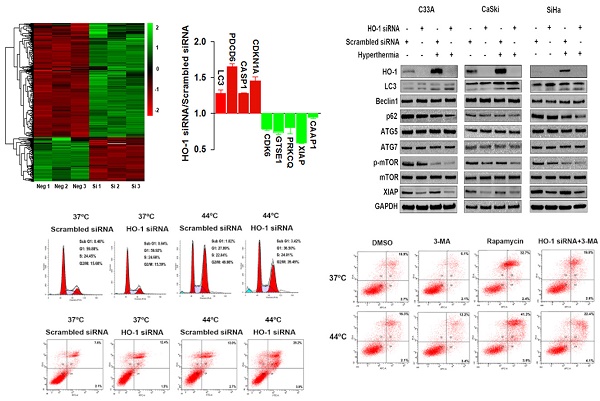
Hyperthermia has been clinically utilized as an adjuvant therapy in the treatment of cervical carcinoma. However, thermotolerance induced by heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), a stress-inducible cytoprotective protein, limits the efficacy of hyperthermic therapy, for which the exact mechanism remains unknown. In the present study, we found that heat treatment induced HO-1 expression and decreased copy number of HPV16 in cervical cancer cells and tissues from cervical cancer and precursor lesions. Knockdown of HO-1 stimulated autophagy accompanied by downregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Furthermore, silencing of HO-1 led to cell intolerance to hyperthermia, as manifested by inhibition of cell viability and induction of autophagic apoptosis. Moreover, HO-1 modulated hyperthermia-induced, autophagy-dependent antiviral effect. Thus, the findings indicate that blockade of HO-1 enhances hyperthermia-induced autophagy, an event resulting in apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through an antiviral mechanism. These observations imply the potential clinical utility of hyperthermia in combination with HO-1 inhibition in the treatment of cervical cancer.
Keywords: Heme oxygenase-1, autophagy, hyperthermia, cervical cancer, human papillomavirus

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact