10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(9):1816-1834. doi:10.7150/ijbs.35520 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Impact of chronically alternating light-dark cycles on circadian clock mediated expression of cancer (glioma)-related genes in the brain
1. The Key Laboratory of Aquatic Biodiversity and Conservation of Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430072, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of the Ministry of Education, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
4. The Department of Cerebrovascular Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China.
5. Henan Medical Key Laboratory of Translational Cerebrovascular Diseases, Zhengzhou, China.
Abstract
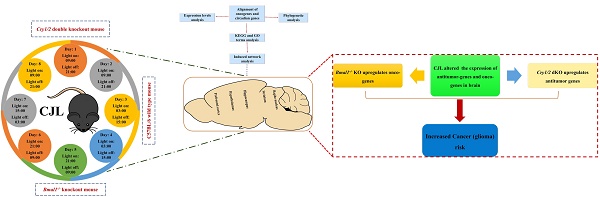
Disruption of the circadian rhythm is a risk factor for cancer, while glioma is a leading contributor to mortality worldwide. Substantial efforts are being undertaken to decrypt underlying molecular pathways. Our understanding of the mechanisms through which disrupted circadian rhythm induces glioma development and progression is incomplete. We, therefore, examined changes in the expression of glioma-related genes in the mouse brain after chronic jetlag (CJL) exposure. A total of 22 candidate tumor suppressor (n= 14) and oncogenes (n= 8) were identified and analyzed for their interaction with clock genes. Both the control and CJL groups were investigated for the expression of candidate genes in the nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, hypothalamus, and striatum of wild type, Bmal1-/- and Cry1/2 double knockout male mice. We found significant variations in the expression of candidate tumor suppressor and oncogenes in the brain tissues after CJL treatment in the wild type, Bmal1-/- and Cry1/2 double knockout mice. In response to CJL treatment, some of the genes were regulated in the wild type, Bmal1-/- and Cry1/2 similarly. However, the expression of some of the genes indicated their association with the functional clock. Overall, our result suggests a link between CJL and gliomas risk at least partially dependent on the circadian clock. However, further studies are needed to investigate the molecular mechanism associated with CJL and gliomas.
Keywords: Circadian Rhythm, Clock Genes, Glioma, Oncogenes, Tumor Suppressor Genes.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact