10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(3):420-434. doi:10.7150/ijbs.37421 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Gut Microbiota as Diagnostic Tools for Mirroring Disease Progression and Circulating Nephrotoxin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease: Discovery and Validation Study
1. Department of Nephrology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan
2. College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan
3. Kidney Research Center, Department of Nephrology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkuo, Taiwan
4. Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University, Florida, US
5. Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan
6. Biotools, Co., Ltd, New Taipei City, Taiwan
7. Institute of Statistics, National Tsing-Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
8. Whole-Genome Research Core Laboratory of Human Diseases, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan
9. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Division of Biotechnology, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan
10. Microbiota Research Center, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Abstract
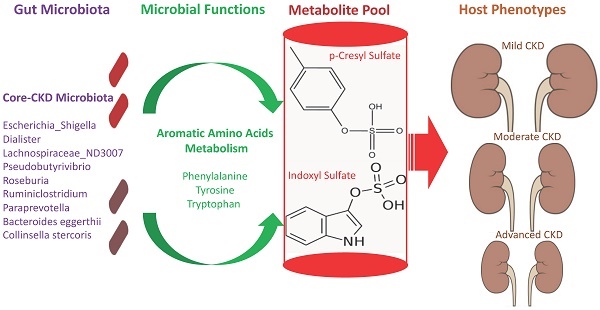
The interplay of the gut microbes with gut-producing nephrotoxins and the renal progression remains unclear in large human cohort. Significant compositional and functional differences in the intestinal microbiota (by 16S rRNA gene sequencing) were noted among 30 controls and 92 (31 mild, 30 moderate and 31 advanced) patients at different chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages (discovery cohort). A core CKD-associated microbiota consisted of 7 genera (Escherichia_Shigella, Dialister, Lachnospiraceae_ND3007_group, Pseudobutyrivibrio, Roseburia, Paraprevotella and Ruminiclostridium) and 2 species (Collinsella stercoris and Bacteroides eggerthii) were identified to be highly correlated with the stages of CKD. Paraprevotella, Pseudobutyrivibrio and Collinsella stercoris were superior in discriminating CKD from the controls than the use of urine protein/creatinine ratio, even at early-stage of disease. The performance was further confirmed in a validation cohort comprising 22 controls and 76 peritoneal dialysis patients. Bacterial genera highly correlated with indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate levels were identified. Prediction of the functional capabilities of microbial communities showed that microbial genes related to the metabolism of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan) were differentially enriched among the control and different CKD stages. Collectively, our results provide solid human evidence of the impact of gut-metabolite-kidney axis on the severity of chronic kidney disease and highlight a usefulness of specific gut microorganisms as possible disease differentiate marker of this global health burden.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease, gut microbiome, p-cresyl sulfate, and indoxyl sulfate

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact