10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(6):957-969. doi:10.7150/ijbs.38264 This issue Cite
Review
Innate Lymphoid Cells at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Human Pregnancy
1. Laboratory for Reproductive Immunology, NHC Key Lab of Reproduction Regulation (Shanghai Institute of Planned Parenthood Research), Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University Shanghai Medical College, Shanghai 200082, People's Republic of China.
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Female Reproductive Endocrine Related Diseases, Shanghai, 200011, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
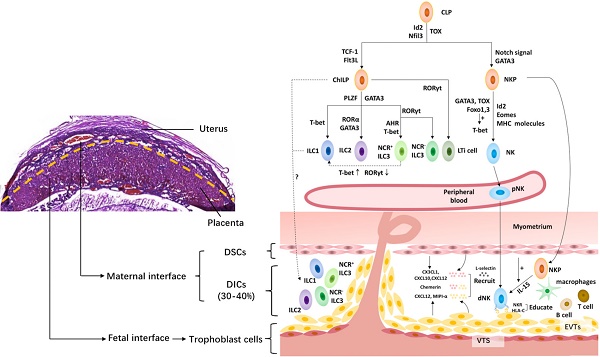
Pregnancy constitutes a major challenge to the maternal immune system, which must tolerate fetal alloantigen encoded by paternal genes. In addition to their role in inducing maternal-fetal immune tolerance, accumulating evidence indicates that decidual immune cells are involved in several processes required for a successful pregnancy, including trophoblast invasion as well as tissue and spiral artery remodeling. Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), an important branch of the innate immune system, which has expanded rapidly in recent years, are strong actors in mucosal immunity, tissue homeostasis and metabolism regulation. With the recent identification of ILCs in the human decidua, the role of ILCs at the maternal-fetal interface raises concern. Herein, we review the presence and characterization of ILCs in the human decidua, as well as their function in normal pregnancy and pathological pregnancy, including reproductive failure, preeclampsia and others.
Keywords: innate lymphoid cell, pregnancy, trophoblast invasion, spiral artery remodeling, reproductive failure, preeclampsia.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact