ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(12):2159-2169. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45933 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA-4516 suppresses pancreatic cancer development via negatively regulating orthodenticle homeobox 1
1. Department of General Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an Jiaotong University, PR China
2. School of Science, Xi'an Jiaotong University, PR China
3. School of Life Science, Xiamen University, PR China
4. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an Jiaotong University, PR China
*These authors contribute equally.
Abstract
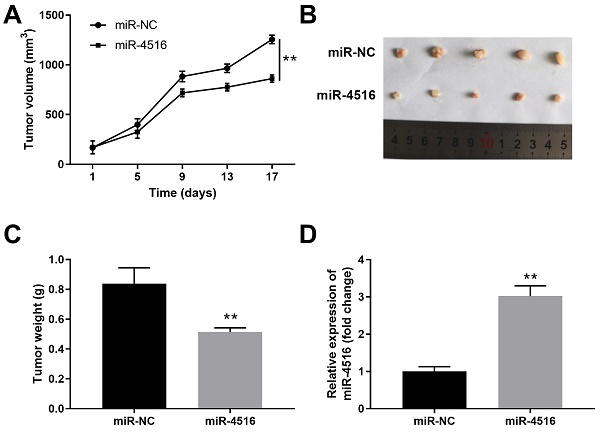
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most lethal human cancers without efficient therapeutic strategy. MicoRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small non-coding RNAs involved in multiple biological processes including tumor development and progression. In this study, we investigated the expression and function of miR-4516 in pancreatic cancer. MiR-4516 was low-expressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-4516 inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, while promoted cell apoptosis in vitro. Further, overexpression of miR-4516 suppressed xenograft pancreatic tumor growth in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis was performed and miR-4516 was predicted to negatively regulate orthodenticle homeobox 1 (OTX1) expression by binding to its 3'-UTR. Consistently, OTX1 was highly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of OTX1 expression suppressed pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion, with down-regulated MMP2 and MMP9 expression. Moreover, we demonstrated that miR-4516 regulated pancreatic cancer cell growth, migration, invasion and apoptosis via targeting OTX1. Overexpression of OTX1 could partially abrogate the inhibitory effect of miR-4516. Taken together, we conclude that miR-4516 could function as a tumor suppressor via targeting OTX1. These findings suggest that miR-4516/OTX1 axis might be a novel therapeutic target for miRNA-based therapy for pancreatic cancer patients.
Keywords: miR-4516, pancreatic cancer, OTX1, miRNA-based therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact