ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(12):2170-2179. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45967 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Long-term UVA exposure to the eye compromises memory and learning ability in mice via corticotropin-releasing hormone type 2 receptor
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Suzuka University of Medical Science, Suzuka, Mie, Japan
Abstract
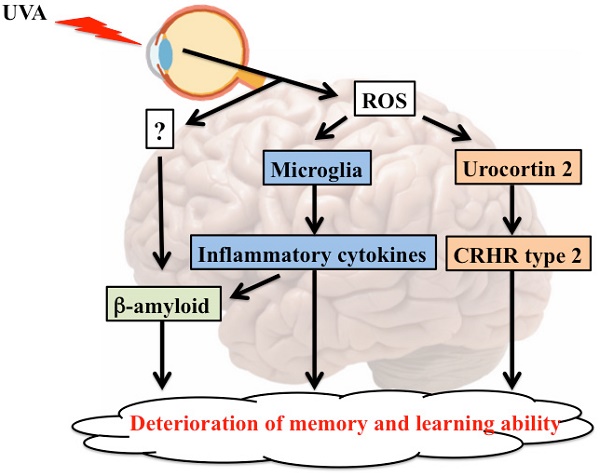
Long-term eye exposure to ultraviolet (UV)A can effect memory and learning ability. However, the underlying mechanism behind these effects remain unknown. In this study, we used HR-1 mice to study effects of long-term UVA eye irradiation. The eyes or dorsal skin of the mice were exposed to UVA at the dose of 110kj/m2 using an FL20SBLB-A lamp three times a week over 12 months. We measured the levels of reactive oxygen species, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), urocortin 2, and CRH type 2 receptor (CRHR-2) in the brain of treated and control animals. Their memory and learning ability following exposure to UVA was analyzed by the standard water maze test. Our results showed that the levels of reactive oxygen species, CRH, urocortin 2, and CRHR-2 increased significantly following long-term UVA irradiation, and the effects were more pronounced in animals subjected to eye irradiation than those subjected to dorsal skin irradiation. Furthermore, the UVA exposure led to an increase in the levels of β-amyloid and microglia in the brain. These results indicated that UVA eye irradiation potentially mediated a decline in memory and learning ability via enhancing levels of urocortin 2, microglia, and β-amyloid in the brain.
Keywords: Ultraviolet A, Memory and learning ability, Reactive oxygen species, Corticotropin-releasing hormone, Urocortin 2, Microglia

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact