ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(12):2235-2247. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47225 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PAK4 phosphorylating RUNX1 promotes ERα-positive breast cancer-induced osteolytic bone destruction
1. Department of Cell Biology, Key Laboratory of Cell Biology of National Health Commission of the PRC, and Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology of Ministry of Education of the PRC, China Medical University, No.77, Puhe Road, Shenyang, 110122, Liaoning, China.
2. Department of Breast Surgery, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, 110001, China.
3. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, 110001, China.
Abstract
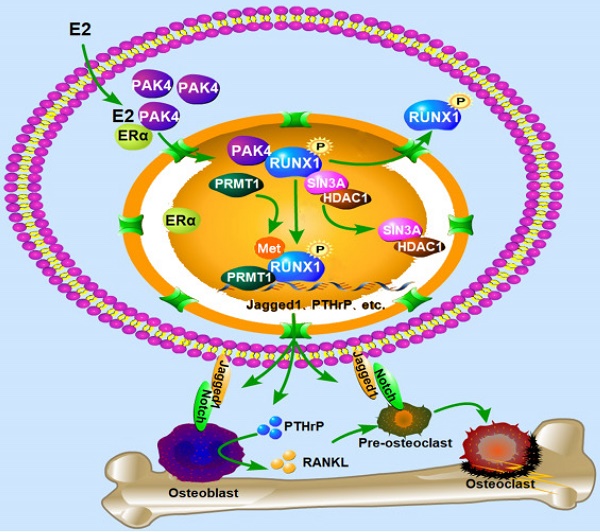
The biological function of nuclear PAK4 in ERα-positive breast cancer osteolytic bone destruction remains unclear. Here, we find that the nuclear PAK4 promotes osteoclastogenesis and tumor-induced osteolysis via phosphorylating RUNX1. We show that nuclear PAK4 interacts with and phosphorylates RUNX1 at Thr-207, which induces its localization from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and influences direct interaction with SIN3A/HDAC1 and PRMT1. Furthermore, we reveal that RUNX1 phosphorylation by PAK4 at Thr-207 promotes osteolytic bone destruction via targeting downstream genes related to osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Importantly, we verify changes in RUNX1 subcellular localization when nuclear PAK4 is positive in breast cancer bone metastasis tissues. Functionally, we demonstrate that RUNX1 phosphorylation promotes osteolytic bone maturation and ERα-positive breast cancer-induced osteolytic bone damage in the mouse model of orthotopic breast cancer bone metastasis. Our results suggest PAK4 can be a therapeutic target for ERα-positive breast cancer osteolytic bone destruction.
Keywords: PAK4, RUNX1, phosphorylation, osteolytic bone destruction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact