10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(16):3116-3132. doi:10.7150/ijbs.42677 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 deficiency effectively protects the brain and neurological function in rodent after acute Hemorrhagic Stroke
1. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung 83301, Taiwan.
2. Institute for Translational Research in Biomedicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung 83301, Taiwan.
3. Center for Shockwave Medicine and Tissue Engineering, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung 83301, Taiwan.
4. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung 40402, Taiwan.
5. Department of Nursing, Asia University, Taichung, 41354, Taiwan.
6. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Xiamen Chang Gung Hospital, Xiamen 361028, Fujian, China.
7. Department of Orthopedics, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung 83301, Taiwan.
8. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
9. Department of Anesthesiology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung 83301, Taiwan.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
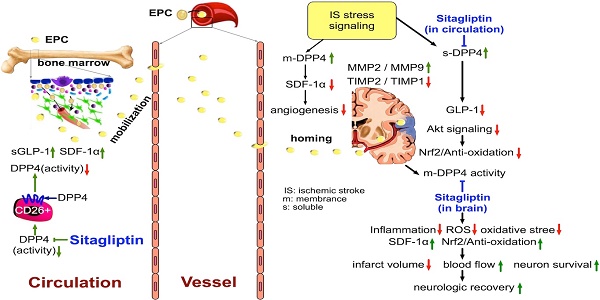
This study tested the hypothesis that abrogated dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) activity played a crucial role on reducing stroke volume and preserving neurological function in rodent after acute hemorrhagic stroke (AHS). Animals (n=6/each group) were categorized into group 1 (sham-control of F344 rat), group 2 (sham-control of DPP4-deficiency rat), group 3 [AHS by right cerebral injection of autologous blood (100 µL) in F344 rat], group 4 (AHS + sitagliptin/600 mg/kg 3 h prior to and at 3 h then once per day after AHS) and group 5 (AHS in DPP4-deficiency rat). The results of corner test showed the neurological function was significantly improved from days 3, 7, and 14 in groups 4 and 5 than in group 3 (all p<0.001). By days 1 and 14 after AHS procedure, the circulating levels of SDF-1α and GLP-1 were significantly increased from groups 1/2 to group 5 (all p<0.001), whereas circulating DPP4 activity was significantly increased in group 3 than other groups (all p<0.001). The brain ischemic area (BIA) was highest in group 3, lowest in groups 1/2 and significantly lower in group 5 than in group 4 (all p<0.0001). The protein expressions of oxidative-stress/inflammatory/apoptotic/cell-proliferation signaling, and the cellular expressions of inflammatory/DNA-damaged biomarkers exhibited a similar pattern to BIA among the groups (all p<0.01). In conclusion, deprivation of DPP4 activity protected the brain from AHS damage and preserved neurological function.
Keywords: acute hemorrhagic stroke, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity, brain infarct area, neurological function, inflammation, angiogenesis, oxidative stress

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact