10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(16):3133-3148. doi:10.7150/ijbs.49520 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Regulation of energy metabolism by combination therapy attenuates cardiac metabolic remodeling in heart failure
1. First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, People's Republic of China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, People's Republic of China.
3. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Translational Research of TCM Prescription and Syndrome, Tianjin, People's Republic of China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
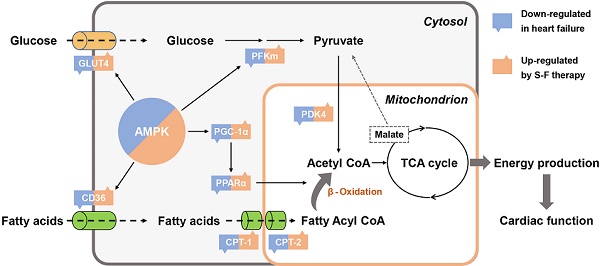
Cardiac metabolic remodeling is recognized as an important hallmark of heart failure (HF), while strategies that target energy metabolism have therapeutic potential in treating HF. Shen-Fu formula (S-F) is a standardized herbal preparation frequently used in clinical practice and is a promising combinatorial therapy for HF-related metabolic remodeling. Herein, we performed an untargeted multi-omics analysis using transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics on HF mice induced by transverse aortic constriction (TAC). Integrated and pathway-driven analyses were used to reveal the therapeutic targets associated with S-F treatment. The cardioprotective effect and potential mechanism of S-F were verified by the results from echocardiography, hemodynamics, histopathology, and biochemical assays. As a result, S-F significantly alleviated myocardial fibrosis and hypertrophy, thus reducing the loss of heart function during adverse cardiac remodeling in TAC mice. Integrated omics analysis showed that S-F synergistically mediated the metabolic flexibility of fatty acids and glucose in cardiac energy metabolism. These effects of S-F were confirmed by the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its downstream targets in the failing heart. Collectively, our results demonstrated that S-F suppressed cardiac metabolic remodeling through activating AMPK-related pathways via energy-dependent mechanisms.
Keywords: cardiovascular systems, energy metabolism, biomarker, multi-omics, combination therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact