10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(16):3149-3162. doi:10.7150/ijbs.46645 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of a novel cancer stem cell subpopulation that promotes progression of human fatal renal cell carcinoma by single-cell RNA-seq analysis
1. Department of Urology, The Gongli Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200135, China
2. Department of Urology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 201805, China
3. Department of Urology, The Changzheng Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
4. Department of Bone Tumor Surgery, The Changzheng Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
5. Department of Anesthesiology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200127, China
6. Department of Urology, The Seventh People's Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200137, China
*These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
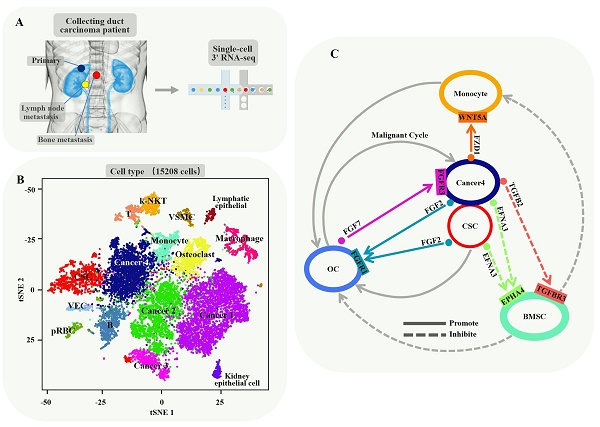
Background: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are biologically characterized by self-renewal, multi-directional differentiation and infinite proliferation, inducing anti-tumor drug resistance and metastasis. In the present study, we attempted to depict the baseline landscape of CSC-mediated biological properties, knowing that it is vital for tumor evolution, anti-tumor drug selection and drug resistance against fatal malignancy.
Methods: We performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis in 15208 cells from a pair of primary and metastatic sites of collecting duct renal cell carcinoma (CDRCC). Cell subpopulations were identified and characterized by t-SNE, RNA velocity, monocle and other computational methods. Statistical analysis of all single-cell sequencing data was performed in R and Python.
Results: A CSC population of 1068 cells was identified and characterized, showing excellent differentiation and self-renewal properties. These CSCs positioned as a center of the differentiation process and transformed into CDRCC primary and metastatic cells in spatial and temporal order, and played a pivotal role in promoting the bone destruction process with a positive feedback loop in the bone metastasis microenvironment. In addition, CSC-specific marker genes BIRC5, PTTG1, CENPF and CDKN3 were observed to be correlated with poor prognosis of CDRCC. Finally, we pinpointed that PARP, PIGF, HDAC2, and FGFR inhibitors for effectively targeting CSCs may be the potential therapeutic strategies for CDRCC.
Conclusion: The results of the present study may shed new light on the identification of CSCs, and help further understand the mechanism underlying drug resistance, differentiation and metastasis in human CDRCC.
Keywords: Collecting duct renal cell carcinoma, Single-cell RNA sequencing, Cancer stem cell, Cellular heterogeneity, Therapeutic strategy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact