ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(5):1315-1327. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58102 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation inhibits its nuclear translocation and promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis
1. Department of Cell Biology, Key Laboratory of Cell Biology of National Health Commission of the PRC, Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology of Ministry of Education of the PRC, China Medical University, No.77, Puhe Road, Shenyang, 110122, Liaoning, China.
2. Department of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Research Unit of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, No. 155, North Nanjing Street, Heping District, 110001 Shenyang, Liaoning, China.
3. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
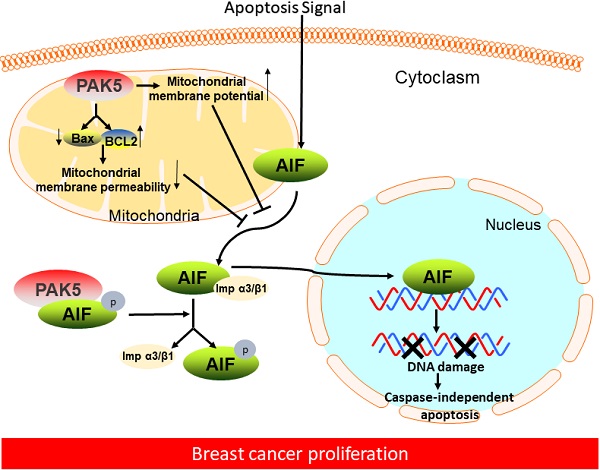
Although p21 activated kinase 5 (PAK5) is related to the progression of multiple cancers, its biological function in breast cancer remains unclear. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is a vital apoptosis factor in mitochondria, which can be released from mitochondria and enter the nucleus, causing caspase-independent apoptosis. In this study, we reveal that PAK5 inhibits apoptosis by preventing the nuclear translocation of AIF. PAK5 inhibits the release of AIF from mitochondria in breast cancer cells by decreasing the mitochondria membrane permeability and increasing the membrane potential. Furthermore, PAK5 phosphorylates AIF at Thr281 site to inhibit the formation of AIF/importin α3 complex, leading to decrease AIF nuclear translocation. Functionally, we demonstrate that PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells and accelerates the growth of breast cancer in vivo. Significantly, PAK5 and AIF expression in breast cancer are positively correlated with poor patient prognosis. PAK5 expression is negatively correlated with AIF nuclear translocation. These results suggest that PAK5-AIF signaling pathway may play an essential role in mammary tumorigenesis, providing a new therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: PAK5, AIF, breast cancer, apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact