10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(5):1361-1381. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58773 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Application of phototherapeutic-based nanoparticles in colorectal cancer
1. Bioinformatics Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China.
2. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China.
3. School of Pharmacy, Henan University, Kaifeng Kaifeng 475004, China.
4. Guangming Substation of Shenzhen Ecological Environment Monitoring Station, Shenzhen 518107, P. R. China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
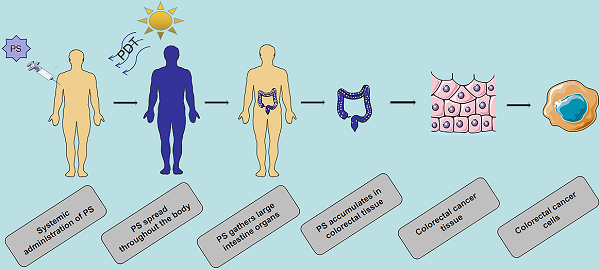
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed malignancy and the second leading cause of cancer death, which accounts for approximately 10% of all new cancer cases worldwide. Surgery is the main method for treatment of early-stage CRC. However, it is not effective for most metastatic tumors, and new treatment and diagnosis strategies need to be developed. Photosensitizers (PSs) play an important role in the treatment of CRC. Phototherapy also has a broad prospect in the treatment of CRC because of its low invasiveness and low toxicity. However, most PSs are associated with limitations including poor solubility, poor selectivity and high toxicity. The application of nanomaterials in PSs has added many advantages, including increased solubility, bioavailability, targeting, stability and low toxicity. In this review, based on phototherapy, we discuss the characteristics and development progress of PSs, the targeting of PSs at organ, cell and molecular levels, and the current methods of optimizing PSs, especially the application of nanoparticles as carriers in CRC. We introduce the photosensitizer (PS) targeting process in photodynamic therapy (PDT), the damage mechanism of PDT, and the application of classic PS in CRC. The action process and damage mechanism of photothermal therapy (PTT) and the types of ablation agents. In addition, we present the imaging examination and the application of PDT / PTT in tumor, including (fluorescence imaging, photoacoustic imaging, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, nuclear imaging) to provide the basis for the early diagnosis of CRC. Notably, single phototherapy has several limitations in vivo, especially for deep tumors. Here, we discuss the advantages of the combination therapy of PDT and PTT compared with the single therapy. At the same time, this review summarizes the clinical application of PS in CRC. Although a variety of nanomaterials are in the research and development stage, few of them are actually on the market, they will show great advantages in the treatment of CRC in the near future.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, photosensitizer, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, nanoparticle.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact