10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(15):4305-4315. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65588 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CD38 Deficiency Protects Mice from High Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Activating NAD+/Sirtuins Signaling Pathways-Mediated Inhibition of Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress in Hepatocytes
1. National Engineering Research Center for Bioengineering Drugs and the Technologies, Institute of Translational Medicine.
2. School of Pharmacy, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, P.R. China.
3. School of Life Science, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, P.R. China.
4. Research Laboratory of Emergency Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, P.R. China.
*These authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
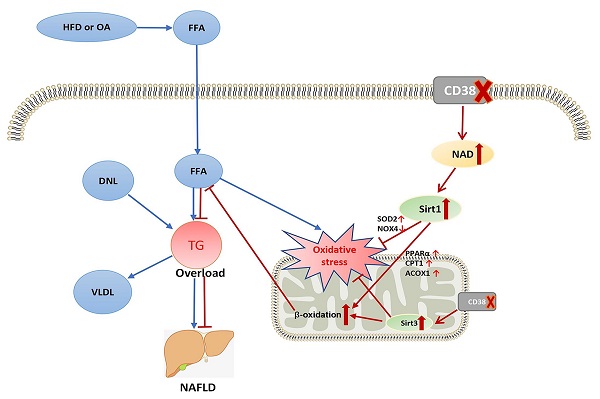
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. CD38 was initially identified as a lymphocyte surface antigen and then has been found to exist in a variety of cell types. Our previous studies showed that CD38-/- mice were resistant to high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity. However, the role and mechanism of CD38 in HFD-induced NAFLD is still unclear. Here, we reported that CD38-/- mice significantly alleviated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. HFD or oleic acid (OA) remarkably increased the mRNA and protein expressions of CD38 in mouse hepatic tissues and primary hepatocytes or hepatic cell lines in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that CD38 might play a role in HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. We observed that CD38 deficiency markedly decreased HFD- or OA-induced the lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in CD38-/- livers or primary hepatocytes, respectively. In contrast, overexpression of CD38 in Hep1-6 cells aggravated OA-induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress. Furthermore, CD38 deficiency markedly inhibited HFD- or OA-induced the expressions of NOX4, and increased the expression of PPARα, CPT1, ACOX1 and SOD2 in liver tissue and hepatocytes from CD38-/- mice, indicating that CD38 deficiency-mediated the enhancement of fatty acid oxidation and the inhibition of oxidative stress contributed to protecting NAFLD. More importantly, Ex527 (Sirt1 inhibitor) and 3-TYP (Sirt3 inhibitor) significantly enhanced OA-induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in CD38-/- primary hepatocytes, suggesting that the anti-lipid accumulation of CD38 deficiency might be dependent on NAD/Sirtuins-mediated enhancement of FAA β-oxidation and suppression of oxidative stress in hepatocytes. In conclusion, we demonstrated that CD38 deficiency protected mice from HFD-induced NAFLD by reducing lipid accumulation and suppressing oxidative stress via activating NAD/Sirtuins signaling pathways.
Keywords: CD38, Sirtuins, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, oxidative stress, lipid accumulation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact