10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(15):4377-4395. doi:10.7150/ijbs.63390 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Secretion of HLA-E by Trophoblasts Maintains Pregnancy by Regulating the Metabolism of Decidual NK Cells
1. Assisted Reproduction Unit, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 310016, Hangzhou, China
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Key Laboratory of Reproductive Dysfunction, Management of Zhejiang Province, 310016, Hangzhou, China
3. Department of Medical, Jiaxing University Affiliated Women and Children Hospital, 314051, Jiaxing, China
4. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hangzhou Women's Hospital, 310008, Hangzhou, China
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
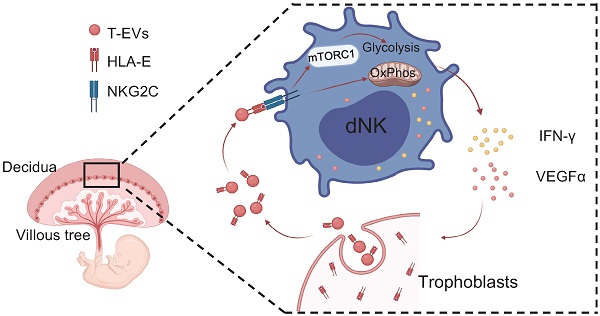
Extracellular vesicles derived from trophoblasts (T-EVs) play an important role in pregnancy, but the mechanism is not entirely clear. In this study, we found that HLA-E, which is mostly confined to the cytoplasm of trophoblast cells, was secreted by T-EVs. The level of HLA-E in T-EVs from unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (URSA) patients was lower than that in normal pregnancy (NP) and RSA patients who had an abnormal embryo karyotype (AK-RSA). T-EVs promoted secretion of IFN-γ and VEGFα by decidual NK (dNK) cells from URSA patients via HLA-E, VEGFα was necessary for angiogenesis and trophoblast growth, and IFN-γ inhibited Th17 induction. Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) were involved in this process. Glycolysis but not OxPhos of dNK cells facilitated by T-EVs was dependent on mTORC1 activation. Inhibition of T-EV production in vivo increased the susceptibility of mice to embryo absorption, which was reversed by transferring exogenous T-EVs. T-EVs promoted secretion of IFN-γ and VEGFα by dNK cells to maintain pregnancy via Qa-1 in abortion-prone mouse models. This study reveals a new mechanism of pregnancy maintenance mediated by HLA-E via T-EVs.
Keywords: Extracellular Vesicles, decidual NK Cells, secretion, HLA-E, pregnancy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact